
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
The β-lactam antibiotics, macrolides
The β-lactam antibiotics, macrolides
1 Analyze the possible points of action of penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides, carbapenems and monobactams in the microbial cells and correlate this with the type of antimicrobial action.
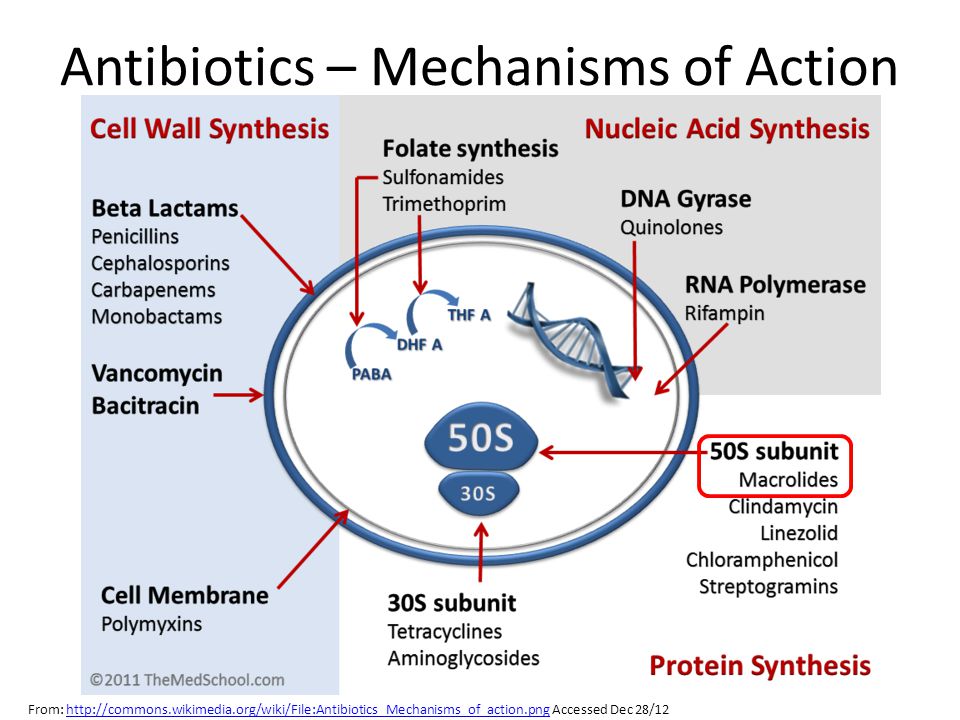
2. Explain the mechanism and type of antibacterial action of β-lactam anti-biotics by placing the following statements in the correct sequence.
А. When susceptible bacteria divide —cell wall deficient (CWD) forms are produced.
B.The β-lactam antibiotics inhibit the transpeptidases
C. Cross linking (which maintains the close knit structure of the cell wall) does not take place.
D. The CWD forms swell and burst → bacterial lysis occurs..
Answer the question:
Why are the β-lactam antibiotics low toxic for macroorganisms?
What is the reason for the rapid development of the resistance?
What is the inhibitor-protected penicillins (cephalosporins)?
3. Determine the spectrum of action of drugs and fill in the table:
| Spectrum | Penicillin G | Oxacillin /Cloxacillin | Amoxicillin | Carbenicillin ticarcillin, piperacillin |
| Streptococci, pneumococci, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and meningitides, staphylococci, producing penicillinase | ||||
| Staphylococci, producing penicillinase | ||||
| B. anthracis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae | ||||
| Treponema pallidum, LeptospiraBorrelia | ||||
| Clostridia | ||||
| H. influenzae, E. coli, Proteus, Salmonella, Shigella and Helicobacter pylori | ||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacteroides |
4. Analyze the pattern changes in concentrations of antibiotics in the blood, determine the drugs А, В, С (Penicillin G, benzathine penicillin, benzylpenicillin procaine). The drugs (500 000 ED) were injected intramuscularly. которые вводили внутримышечно в дозе 500 000ЕД. explain the differences in pharmacokinetics and indicate the possible multiplicity of the introduction 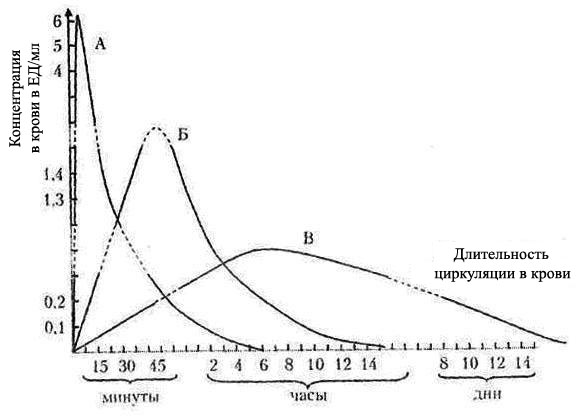
5. Determine semi-synthetic penicillins (ampicillin, Amoxiclav, cloxacillin, carbenicillin):
| Drugs | Spectrum | Resistance to Penicillinase | Inhibitor protected | Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
| Narrow (Gram +) | Wide (gram - , gram +) | ||||
| А | + | - | - | + | |
| B | + | + | - | - | |
| C | + | + | + | - | |
| D | + | - | - | - | |
6. Choose a treatment: Syphilis, Rheumatic fever, Tetanus and gas gangrene, Streptococcal and Pneumococcal infections ( pharyngitis, otitis media, bronchitis, sinusitis) , Urinary tract infections, Bacillary dysentery, infections caused by penicillinase producing Staphylococci, infections caused by H. pylori, infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Gonorrhoea
Penicillin G, benzathine penicillin, Amoxiclav, amoxicillin, piperacilline, cloxacillin, ampicillin
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|