
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
The pituitary and hypothalamus are connected by the pituitary foot
The pituitary and hypothalamus are connected by the pituitary foot
• Hypothalamus - ventral part of the diencephalon
• The pituitary gland is the "central gland" of internal secretion, regulates the work of other endocrine glands
The pituitary and hypothalamus are connected by the pituitary foot
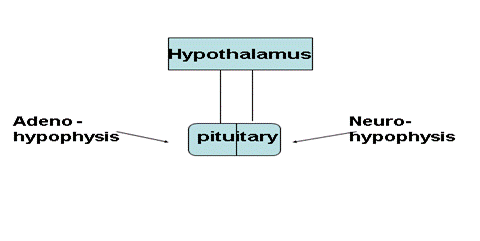
Hormones of adenohypophysis:
STH (somatotropic hormone) affects bone and cartilage tissue, enhances protein synthesis
Prolactin affects milk production in the mammary gland
MSH (melanocyte-stimulating hormone) controls pigment metabolism
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) acts on the thyroid gland, increases the production of the hormone thyroxine.
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) stimulates the formation of glucocorticoids in the adrenal cortex.
GTG (gonadotropic hormones):
1) FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) - affects follicles in women and spermatogenesis in men.
2) LH (luteinizing hormone) stimulates the growth of the follicle, the formation of estrogens in women and androgens in men.
The releasing hormones (liberins, statins) secreted by the hypothalamus on the principle of feedback regulate the production of tropic hormones
Hormones of the neurohypophysis:
Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone -ADG)affects the reabsorption of water in the kidneys, in addition, narrows the vessels. Isolation of it into the blood occurs under the influence of impulses from the hypothalamus as the osmotic pressure of the blood increases
Oxytocinstimulates the musculature of the uterus, stimulates the excretion of milk.
Thyroid function:
Hormones: thyroxine, triiodothyronine have a strong influence on the growth and development of the child's body, in particular the central nervous system, control the basal metabolism, stimulate the breakdown of fat, glycogen; increase heart rate, blood pressure, puls, sweating.
Thyreocalcitonin lowers the calcium content in the blood, reducing its reabsorption in the kidneys and absorption in the intestines, translates into bones.
When the thyroid gland is damaged, the hard tissues of the tooth change.
Acquired hypothyroidism - endemic goiter: caries, dental anomalies, mucosal edema.
Congenital hypothyroidism - delay of eruption of milk teeth, change of milk teeth by constant, underdevelopment of crowns, rapid abrasion of them, adentia, deformation of jaws.
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|