
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Data collection. Data collection details
Data collection
Overview of data collection is presented in Figure 2. Only admission data, results of diagnostic methods, final diagnosis and hospital survival will be collected for patients in whom AMI was suspected but not confirmed.
Figure 2. Data collection
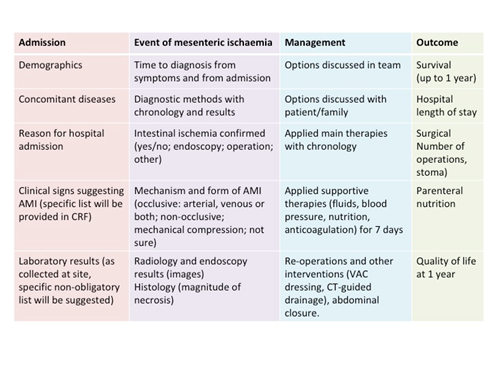
Data collection details
Baseline data
Demographics
Ethnicity
Gender (M/F)
Age (y)
Weight (kg)
Height (cm)
BMI (kg/m2)
Chronic health conditions
Disability (no need of assistance/needs/No information(NI))
Smoking (yes/no/NI)
Atrial Fibrillation (yes/no/NI)
Atherosclerotic disease (prevalent ischaemic heart disease, stroke, peripheral arterial disease (carotid artery stenosis, lower extremity arterial disease such as claudication or chronic limb-threatening ischaemia/critical limb ischaemia) (yes/no/NI)
Arterial hypertension (yes/no/NI)
Previous myocardial infarction (yes/no/NI)
Previous arterial thromboembolic events (yes/no/NI)
Artificial heart valve (yes/no/NI)
Medications at home
Anticoagulant drugs (yes/no/NI)
Antiplatelet drugs (yes/no/NI)
Statins (yes/no/NI)
Emergency Department (ED) data
Means of arrival to the hospital (by self, ambulance)
Time to arrival at the hospital from the beginning of symptoms (hours (h)/unclear)
Initial diagnosis leading to hospital admission
Type of ED where the patient was initially admitted (surgical/non-surgical/mixed = no separated surgical/non-surgical)
Acute health condition at admission or immediately before the diagnosis of AMI (if AMI suspected/diagnosed later during the hospital stay)
Charlson co-morbidity index with a link to respective calculator
APACHE II (only if patient is hospitalized to the ICU) with a link to respective calculator
New (previously not documented) atrial fibrillation
Cardiac arrest (yes/no, prehospital setting/emergency room/in-hospital)
Mechanical ventilation (initiated in prehospital setting/emergency room)
Vasopressors with maximum dosage within 72h before the diagnosis of AMI
Maximum intra-abdominal pressure within 72h before the diagnosis of AMI
Main symptoms
Symptoms causing hospital admission
Symptoms supporting suspicion of AMI
acute abdominal pain
diarrhoea
bloody stools
shock
other (specify)
Acute conditions (during this hospitalisation) with known risk of AMI
cardiac surgery
aortic surgery
embolisation of mesenteric arteries/branches (e. g. due to bleeding)
shock with high-dose vasopressors (document max dose)
Laboratory tests on hospital admission day or at the time suspicion of AMI arises (if taken)
Lactate (mmol/l/NI)
· highest during 48-72h before the diagnosis of AMI (if applicable)
· highest during 24-48h before the diagnosis of AMI (if applicable)
· highest during 12-24h before the diagnosis of AMI (if applicable)
· highest during 0-12h before the diagnosis of AMI
WBC (x 10E9/L/NI), maximal or minimal (most pathologic) within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
Creatinine (mcmol/l/NI), maximal within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
eGFR (mL/min/1, 73m27/NI), minimal within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
pH, minimal within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
BE (mmol/l/NI), worstwithin 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
ASAT (U/L/NI), maximal within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
Amylase (U/L/NI), maximal within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
C-reactive protein (mg/L)
D-dimers (mg/L/NI), maximal within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
Troponin T (ng/L/NI), maximum within 72 hours before the diagnosis of AMI, if several measurements performed
AMI event data
AMI occurred during hospital treatment (Y/N) If YES here, answer specific questions:
Location in the hospital (medical ward, surgical ward, HDU, ICU, other)
Time from hospital admission until suspicion of AMI (days, h if < 24h)
Time from hospital admission (from suspicion of AMI if AMI occurred during the hospital stay) to CT-scan (h)
Time from beginning of symptoms to diagnosis of AMI (h)
Specialty of physician performing the first evaluation after beginning of symptoms (surgery, medicine, emergency medicine, critical care, other)
Time from arrival to the hospital to diagnosis of AMI (in ED patients)(h)
AMI was admission diagnosis in case of referral from another hospital (patient referred for treatment) (Y/N)
Surgery during the hospital stay before diagnosis of AMI
Factors leading to delay in diagnosis (high workload, nonspecific symptoms, normal lactate value, insufficient experience regarding AMI of the first specialist, no predisposing factors identified, other (specify))
Radiological imaging
What was the first radiographic study (x-ray, US, CT, other, none)
Was AMI suspected in the referral for first radiographic study?
Was a CT-scan performed (yes/no)
Phases of enhancement in CT-scan (no contrast media, portal venous, arterial,
delayed phase)
Radiologist diagnosed AMI (yes/no/uncertain)
Time between CT-scan and the response by radiologist (min)
Type of AMI
arterial embolism (localization)
arterial thrombosis (localization)
arterial non-specified (localization)
venous (localization)
NOMI (localization)
Mechanical compression
Other/Unclear (localization)
Management data
Treatment options NOT available at the time of diagnosis
endovascular revascularisation
intra-arterial vasodilation
other (specify)
Treatment options discussed within the team (multiple options possible)
exploratory laparotomy
endovascular revascularisation
endovascular revascularisation followed by open visceral surgery
open surgical revascularisation with or without intestinal resection
Intestinal resection without revascularisation
intra-arterial vasodilation
palliation
other (specify)
Treatment options discussed with patient and family
exploratory laparotomy
endovascular approach
open surgery
endovascular approach plus surgery
palliation
Initial treatment of AMI
Time from beginning of symptoms to each specific treatment of AMI (h)
Time from presentation (arrival at the hospital) to treatment (h)
Time from diagnosis to treatment (h)
Surgical management (explorative laparoscopy, explorative laparotomy, therapeutic
laparotomy, damage control)
Surgical revascularization (embolectomy, thrombectomy, endarterectomy,
aortomesenteric shunt, ROMS, other)
Endovascular treatment (aspiration of thrombus/embolism, balloon dilatation,
stenting, thrombolysis, intraarterial vasodilation, other, combined)
Gastrointestinal tract surgical management (no need, resection with primary anastomosis, resectionwith stoma formation, resection without anastomosis and planned second look)
Small intestinal resection (cm/NI)
Length of residual small intestine (cm/> 200cm/NI)
Resection of colon (no need, right hemicolectomy, left hemicolectomy or sigmoid resection subtotal or total colectomy, other)
Open abdomen (yes/no)
Conservative treatment (yes/no)
End-of-life care
Later surgical treatment
Pre-planned second-look laparotomy
Number of re-operations
Number of other interventions (specify)
Time to closure if open abdomen
Systemic treatment after diagnosis/treatment of AMI (after treatment of AMI, or diagnosis of AMI if no specific intervention was applied (e. g. NOMI without mesenteric infarction))
SOFA score with all subscores separately (only if patient is hospitalized to the ICU)
Vasopressors (maximum dosage during 48h)
Fluids(total i/v fluids and maximum positive fluid balance during 48h after treatment of AMI)
Mechanical ventilation (yes/no, days)
Renal replacement therapy (yes/no, days)
Nutrition (oral/enteral/parenteral/combined/none, total calories within 48h)
Anticoagulation(specific medication and maximal target dosage within 48h)
Antiplatelet therapy (specific medications)
Histology data on (if available)
Sample from initial operation/reoperation
transmural necrosis present
only mucosal necrosis present
other (specify)
Outcome data
Only hospital survival and no other outcomes will be documented for patients with suspected but not confirmed AMI.
For patients with confirmed AMI, the following outcome data will be collected:
· at hospital discharge: hospital survival, hospital stay, ICU stay, duration of parenteral nutrition (PN) in hospital, home PN initiated, stoma
· at 30 days: survival
· at 90 days: survival, home PN, stoma
· at 1 year: survival, physical independency/quality of life (EQ-5D-5L) (11).
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|