
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Types of court. Persons in Court
Types of court
6. Match each of the following types of court (1-9) with the explanation of what happens there (a-i).
| 1. appellate court (or court of appeals, appeals court) 2. crown court 3. high court (or supreme court) 4. juvenile court 5. lower court (or court of first instance) 6. magistrates' court 7. moot court 8. small-claims court 9. tribunal | a This is where a person under the age of 18 would be tried. b This is the court of primary jurisdiction, where a case is heard for the first time. c This is where small crimes are tried in the UK. d This is where law students argue hypothetical cases. eThis is where a case is reviewed which has already been heard in a lower court. f This is where cases involving a limited amount of money are handled. g This is where serious criminal cases are heard by a judge and a jury in the UK. h This is where a group of specially chosen people examine legal problems of a particular type, such as employment disputes. i This is usually the highest court in a jurisdiction, the court of last resort. |
Persons in Court
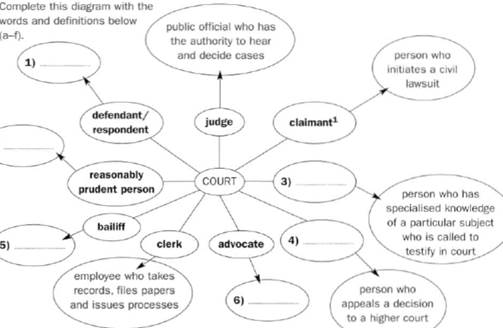
| a expert witness b appellant (petitioner) c person who is sued in a civil lawsuit d officer of the court whose duties include keeping order and assisting the judge and jurors e person who pleads cases in court f hypothetical person who uses good judgment or common sense in handling practical matters: such a person's actions are the guide in determining whether an individual's actions were reasonable |
7. Listen to a lawyer telling a client about some of the documents involved in his case and answer these questions.
1. What claim has been filed against the client?
2. Will the case go to trial?
8. Match these documents (1-9) with their definitions (a-i).
| 1. affidavit 2. answer 3. brief 4. complaint 5. injunction 6. motion 7. notice 8. pleading 9. writ | a. a document informing someone that they will be involved in a legal process b. a document or set of documents containing the details about a court case c. a document providing notification of a fact, claim or proceeding d. a formal written statement setting forth the cause of action or the defence in a case e. a written statement that somebody makes after they have sworn officially to tell the truth f. an application to a court to obtain an order, ruling or decision g. an official order from a court for a person to stop doing something h. in civil law, the first pleading filed on behalf of a plaintiff, which initiates a lawsuit, setting forth the facts on which the claim is based i. the principal pleading by the defendant in response to a complaint |
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|