
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Chapter 21. EV = (P1 × S1) + (P2 × S2) + . . . + (PN × SN). (Probability of state S × Total utility in state S). = (0.5 × UH) + (0.5 × US)
Chapter 21
A random variable is a variable with an uncertain future value.
The expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values, where the weights on each possible value correspond to the probability of that value occurring.
A state of the world is a possible future event.
Risk is uncertainty about future outcomes. When the uncertainty is about monetary outcomes, it becomes financial risk.
Expected value of a random variable
EV = (P1 × S1) + (P2 × S2) +. . . + (PN × SN)
Expected utility is the expected value of an individual’s total utility given uncertainty about future outcomes.
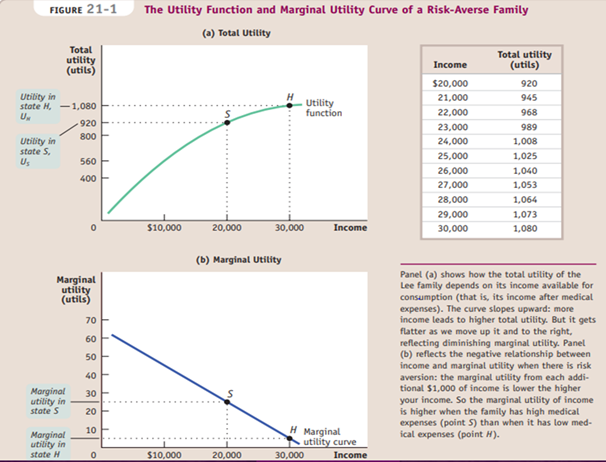
A premium is a payment to an insurance company in return for the insurance company’s promise to pay a claim in certain states of the world.
A fair insurance policy is an insurance policy for which the premium is equal to the expected value of the claim.
Risk-averse individuals will choose to reduce the risk they face when that reduction leaves the expected value of their income or wealth unchanged.
Expected utility
(Probability of state H × Total utility in state H) +
(Probability of state S × Total utility in state S)
= (0. 5 × UH) + (0. 5 × US)
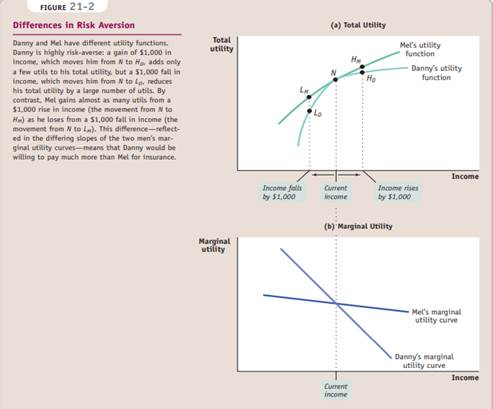
The funds that an insurer places at risk when providing insurance is called the insurer’scapital at risk.
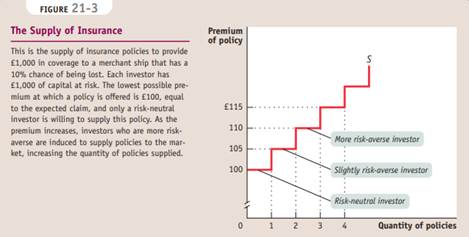
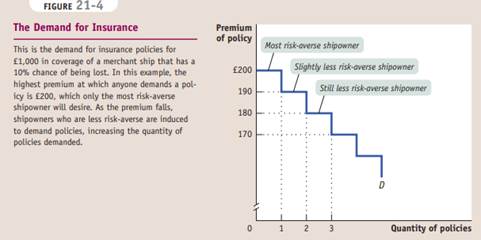
An efficient allocation of risk is an allocation of risk in which those who are most willing to bear risk are those who end up bearing it.
Two possible events are independent events if each of them is neither more nor less likely to happen if the other one happens.
An individual can engage in diversification by investing in several different things, so that the possible losses are independent events.
A share in a company is a partial ownership of that company.
Pooling is a strong form of diversification in which an investor takes a small share of the risk in many independent events. This produces a payoff with very little total overall risk.
Two events are positively correlated if each event is more likely to occur if the other event also occurs.
Private information is information that some people have that others do not.
Adverse selection occurs when an individual knows more about the way things are than other people do. Private information leads buyers to expect hidden problems in items offered for sale, leading to low prices and the best items being kept off the market.
Adverse selection can be reduced through screening: using observable information about people to make inferences about their private information.
Adverse selection can be diminished by people signaling their private information through actions that credibly reveal what they know.
A long-term reputation allows an individual to reassure others that he or she isn’t concealing adverse private information.
Moral hazard occurs when an individual knows more about his or her own actions than other people do. This leads to a distortion of incentives to take care or to exert effort when someone else bears the costs of the lack of care or effort.
A deductible in an insurance policy is a sum that the insured individual must pay before being compensated for a claim
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|