
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Chapter 18
A good is excludable if the supplier of that good can prevent people who do not pay from consuming it.
A good is a rival in consumption if the same unit of the good cannot be consumed by more than one person at the same time.
A good that is both excludable and rival in consumption is a private good.
When a good is nonexcludable, the supplier cannot prevent consumption by people who do not pay for it.
A good is nonrival in consumption if more than one person can consume the same unit of the good at the same time.
Because goods can be either excludable or nonexcludable, rival or nonrival in consumption, there are four types of goods, illustrated by the matrix in Figure:

Why Markets Can Supply Only Private Goods Efficiently?
Goods that are nonexcludable suffer from the free-rider problem: individuals have no incentive to pay for their own consumption and instead will take a “free ride” on anyone who does pay.
A public good is both nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption.
Here are some other examples of public goods:
1) Disease prevention. When doctors act to stamp out the beginnings of an epidemic before it can spread, they protect people around the world.
2) National defense. A strong military protects all citizens.
3) Scientific research. More knowledge benefits everyone.
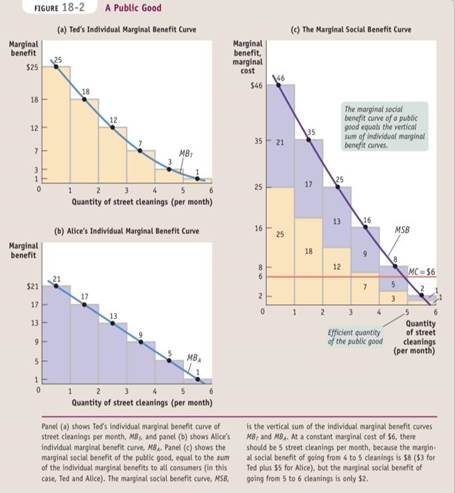
Governments engage in cost-benefit analysis when they estimate the social costs and social benefits of providing a public good.
A common resource is nonexcludable and rival in consumption: you can’t stop me from consuming the good, and more consumption by me means less of the good available for you.
Common resources left to the market suffer from overuse: individuals ignore the fact that their use depletes the amount of the resource remaining for others.
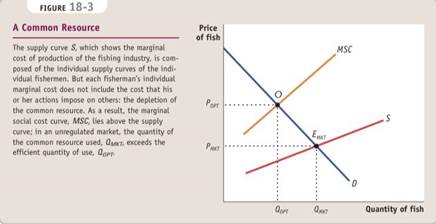
There are three fundamental ways to induce people who use common resources to internalize the costs they impose on others.
Tax or otherwise regulate the use of the common resource
Create a system of tradable licenses for the right to use the common resource
Make the common resource excludable and assign property rights to some individuals
An artificially scarce good is excludable but nonrival in consumption.
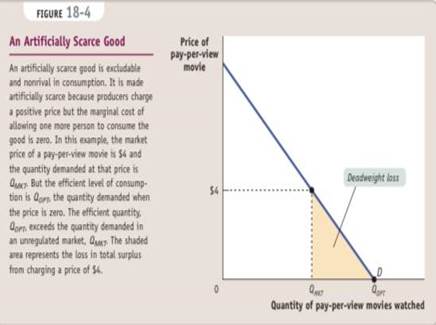
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|