
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
CHAPTER 141-160. Chapter 161-180
CHAPTER 141-160
| 10. Young children with these food allergies have at least a 50% chance of outgrowing them by kindergarten: |
A. Cow's milk and eggs 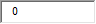
B. Cow's milk and tree nuts 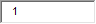
C. Peanuts 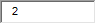
D. Tree nuts 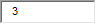
E. Seafood and eggs
| 18. Which disease is incorrectly matched with the characteristic rash? |
A. Systemic lupus erythematosis—malar rash sparing nasolabial folds 
B. Discoid lupus—hyperkeratotic rash around the ears 
C. Kawasaki disease—vesicular rash 
D. Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM)—Gottron papules and heliotrope rash 
E. Henoch-Schö nlein purpura—palpable purpura on extensor surfaces of lower extremities
| 19. Which of the following is medications used in the treatment of rheumatic disorders is NOT disease modifying? |
A. Celecoxib 
B. Cyclophosphamide 
C. Methotrexate 
D. Sulfasalazine 
E. Azathioprine
| 36. Which of the following organ or body systems is least likely to be involved in patients with Behç et disease? |
A. Oropharynx 
B. Joints 
C. Skin 
D. Kidney 
E. Eyes
Chapter 161-180
| 46-Which statement about cephalosporins is FALSE? |
A. Cefazolin is a 1st generation cephalosporin, commonly used in preoperative prophylaxis against skin infections
B. The 2nd generation cephalosporins have additional gram-negative activity as compared with 1st generation cephalosporins
C. Ceftriaxone has good CSF penetration, making it useful in suspected meningitis
D. Of the 3rd-generation cephalosporins, only ceftazidime has activity against P. aeruginosa
E. Cefepime has activity against P. aeruginosa and methicillin-resistant S. aureus
| 47-Linezolid is indicated in the treatment of what infection? |
A. MRSA skin infections also resistant to clindamycin
B. Vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infection (VRE)
C. Highly resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus central line infection
D. S. pneumoniae bacteremia, with resistance to penicillin and clindamycin
E. All of the above
| 55- Scarlet fever is caused by: |
A. Staphylococcus aureus strains that produce exfoliatins
B. Staphylococcus aureus strains that produce enterotoxins
C. Group A streptococcal strains that produce pyrogenic exotoxins
D. Human herpesvirus type 6
E. Parvovirus B19
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|