
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
CHAPTER 81-100
|
A. Familial hypercholesterolemia 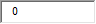
B. Polygenic hyperlipidemia 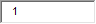
C. Familial combined hyperlipidemia 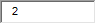
D. Unknown 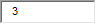
E. Dysbetalipoproteinemia
| 8. A 15 yr old presents with chronic fatigue and severe bone pain of 1 year's duration. He has hepatosplenomegaly and a normal retinal examination. Laboratory studies reveal normocytic anemia and thrombocytopenia. Radiographs of the distal femur reveal Erlenmeyer flask deformities. The most likely diagnosis is: |
A. Lymphoma 
B. Gaucher disease 
C. Sandhoff disease 
D. GM3 gangliosidosis 
E. Sickle cell anemia
| 12. A 7 mo old boy has been healthy and developing normally since birth. His mother now reports that he has decreased eye contact with her, even during feedings. The infant also startles very easily when there is a loud noise in the house. Of the following, the most appropriate diagnostic test to confirm the etiology of these findings is the measurement of: |
A. Leukocyte β -hexosaminidase A activity 
B. Serum concentration of amino acids 
C. Serum concentration of ammonia 
D. Urinary mucopolysaccharides 
E. Urinary organic acids
| 24. A 2 yr old toddler is brought to the emergency department in the morning because he is lethargic. His parents report that he did not eat much dinner the night before. This morning they checked on him at 9 AM, 2 hours after he normally wakes, and they were unable to fully arouse him. In the emergency department, blood glucoselevel is 29 mg/dL and plasma insulin is low. A urine sample is positive for ketones. IV D10W bolus is given with appropriate rise in glucose. In addition to observing the patient take carbohydrates by mouth and documenting normoglycemia, the most appropriate management is: |
A. Advise parents to limit overnight fasting to 10 hours; provide urine dipsticks to check for ketones when the patient is ill 
B. Initiate a ketogenic provocative diet for diagnosis 
C. Admit to hospital to provoke hypoglycemia and send critical sample 
D. Provide reassurance and discharge home 
E. Provide glucometer and advise parents to check fingerstick glucose three time daily
| 25. A 2 week old formula-fed infant presents with poor feeding and somnolence. Examination is notable for microphallus, jaundice, and mild dehydration. Laboratory studies are significant for Na 145 mEq/L, K 3. 4 mEq/L, and glucose 25 mg/dL. Total bilirubin is 13 mg/dL with conjugated fraction of 4. The most likely diagnosis is: |
A. Inadequate feeding leading to jaundice and hypoglycemia 
B. Hypopituitarism 
C. Islet cell adenoma 
D. Munchausen syndrome by proxy 
E. Ketotic hypoglycemia
| 26. A full-term newborn infant with birth weight of 4. 5 kg has a normal Apgar score at birth. On the second day of life, she has a seizure and her blood glucose level is 18 mg/dL. The most appropriate next step in management is to: |
A. Begin prednisone administration 
B. Repeat a mini-bolus of D10W 
C. Give a mini-bolus of D10W plus continuous intravenous glucose infusions 
D. Give continuous intravenous glucose infusion 
E. Administer diazoxide
| 30. Which physical examination finding in a neonate is benign? |
A. Palatal cleft 
B. Grunting and nasal flaring 
C. Hypotonia 
D. White pupillary reflex 
E. Erythema toxicum
| 36. Which of the following is not routine care that should be provided to all term neonates? |
A. Application of anti-gonococcal ophthalmic ointment 
B. Intramuscular injection of vitamin K 
C. Screening hematocrit 
D. Newborn screening for various genetic, metabolic, hematologic, and endocrine disorders 
E. Administration of hepatitis B immunization F. Hearing screen
| 43. Neural tube defects (NTDs) can best be prevented by: |
A. Preconception ingestion of at least 400 µg/day of folic acid 
B. Supplementation of at least 400 µg/day of folic acid from the time of first positive pregnancy test 
C. Supplementation of at least 400 µg/day of folic acid beginning with the first obstetric visit 
D. Eating fortified cereal throughout pregnancy 
E. Taking a prenatal multivitamin throughout pregnancy
| 47. Which statement about twins is not true? |
A. Monovular twinning appears to be an inherited tendency 
B. Most twins are born prematurely 
C. Ninety percent of twins are detected before delivery 
D. Monochorionic twins may be presumed to be monovular 
E. The second born twin is at increased risk for respiratory distress syndrome and asphyxia compared with the first born
| 50. Which of the following statements regarding the assessment of gestational age at birth is NOT true? |
A. In the absence of asphyxia, neurologic maturity correlates with gestational age 
B. The Ballard scoring system is accurate to within 2 days 
C. If a discrepancy exists between the estimation of gestational age by physical examination and fetal ultrasonographic evaluation, the infant is at high risk for morbidity and mortality 
D. Physical features used to assess gestational age include breast buds, ear development, and presence of lanugo
| 77. Which of the following statements regarding neonatal opiate withdrawal is NOT true? |
A. Drug treatment of neonatal withdrawal should be initiated on the basis of withdrawal symptoms 
B. A combination of an opiate plus phenobarbital may be the most effective approach to an opiate withdrawal 
C. Buprenorphine, rather than methadone, treatment during pregnancy reduces the severity and duration of withdrawal 
D. Infants who are undergoing opiate withdrawal require care in a quiet environment with reduction of external stimuli and swaddling 
E. Symptoms of withdrawal include hypothermia and excessive appetite
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|