
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
3 Results
The following algorithm of flexible state management of migration flows in a multicultural region is offered (Figure 1).
| coefficient of tension in the labor market< 1 |
| annual growth rate of load on able-bodied population> 1 |
| in other cases |
| Is there a need for migrants? |
| Monitoring of the number and structure of population (in dynamics) and the labor market in the region |
| There’s a need for labor migrants |
| There’s a need for labor migrants |
| There’s no need and/or the region is overpopulated |
| Stimulation of employment |
| Stimulation of self-employment |
| Canceling of the measures for support for migrants |
| What is the coefficient of migration growth? |
| annual growth rate ≥ 1 |
| annual growth rate < 1 |
| Prevention of violations of law |
| What is the coefficient of migration growth? |
| annual growth rate ≥ 1 |
| annual growth rate< 1 |
| Additional support for migrants |
Figure 1. Algorithm of flexible state management of migration flows in a multicultural region.
Source: developed and compiled by the authors.
As is seen in Figure 1, the initial point of the developed algorithm is monitoring of the number and structure of population (in dynamics) and the labor market in the region. As a result of this monitoring, the multicultural region’s need for migrants is determined. If the annual growth rate of the load on able-bodied population (number of disabled residents of the region per 1, 000 able-bodied residents) exceeds 1, 000 (i. e., the load grew over the recent year), there is a need for labor migrants. In this case, stimulation of employment through mediation of the state (e. g., in the form of the Chamber of trade and commerce of the region) between job applicants and employers is expedient.
If the coefficient of tension in the labor market (number of job applicants per 1 vacant job) is below 1 (deficit of employees), there’s a need for migrants (not necessarily labor migrants). In this case, it is offered to stimulate self-employment by allocating regional grants for creation and development of companies. Then, if the annual growth rate of the coefficient of migration growth per 10, 000 people is below 1 (increase of the incoming flow of migrants in the region is not achieved), it is necessary to additionally support the migrants – e. g., with social benefits, subsidies for rent and purchase of accommodation, etc.
If the need for migrants is absent and/or region is overpopulated, it is necessary to cancel the measures of support for migrants, in order to limit the inflow of migrants into the region and to save the assets of the regional state budget. Then, if the annual growth rate of the coefficient of migration growth per 10, 000 people exceeds or equals 1 (inflow of migrants into the region continues), it is necessary to adopt the measures of prevention of violations of law, which growth is explained by increase of unemployment in the region and reduction of living standards, as well as growth of the share of population with the income below the subsistence level. Then, return to the beginning of the algorithm takes place (the algorithm is cyclic).
The approbation of the developed algorithm by the example of top-3 multicultural regions of Russia in 2018 is performed based on the statistics that are shown in Figure 1.
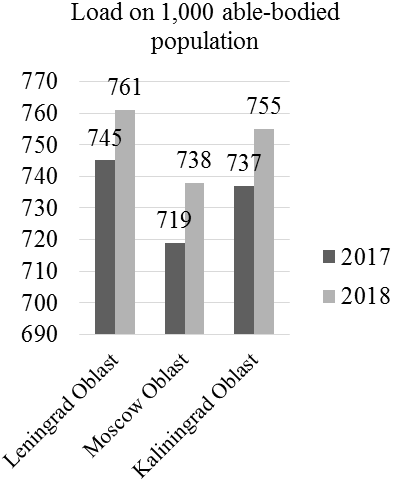
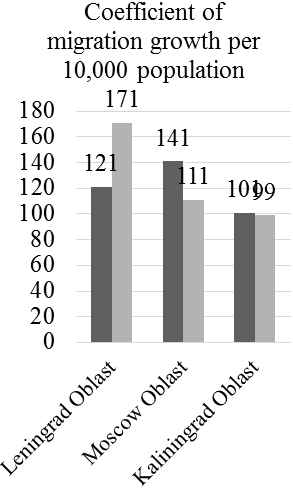
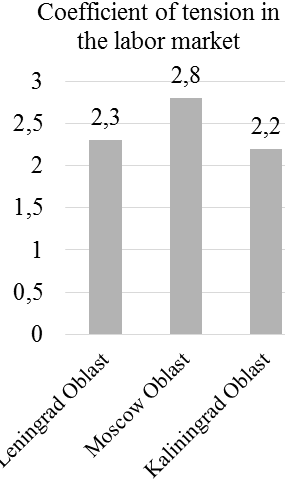
Figure 2. Results of monitoring of the number and structure of population (in dynamics) and the labor market in top-3 multicultural regions of Russia
in 2017-2018.
Source: compiled by the authors based on Federal State Statistics Service (2019).
According to Figure 2, the annual growth rate of the load on able-bodied population in Leningrad Oblast constitutes 1. 02 (761/745), in Moscow Oblast – 1. 03 (738/737), and in Kaliningrad Oblast – 1. 02 (755/737). That’s why it is recommended to stimulate the population’s employment in all regions. The coefficient of tension in the labor market in all regions exceeds 1, constituting 2. 3 in Leningrad Oblast, 2. 8 in Moscow Oblast, and 2. 2 in Kaliningrad Oblast. The annual growth rate of the coefficient of migration growth per 10, 000 people in Leningrad Oblast constitutes 1. 41 (171/121), in Moscow Oblast – 0. 79 (111/141), and in Kaliningrad Oblast – 0. 98 (101/99). That’s why there’s a need for additional support for migrants in Moscow and Kaliningrad Oblasts.
The following algorithm of flexible state management foreign economic activities in a multicultural region is offered (Figure 3).
| What is the growth rate of the number of companies and their turnover? |
| low |
| Stimulation of innovations |
| positive (export exceeds import) |
| negative or zero (import equals or exceeds export) |
| What is the foreign trade balance? |
| Monitoring of foreign economic activities and commodity markets (in dynamics) in the region |
| What is the region’s competitiveness? |
| What is the growth rate of the number of companies and their turnover? |
| high |
| Stimulation of export |
| < 1 |
| Stimulation of import substitution |
| ≥ 1 |
| Limitation of import |
| < 1 |
| ≥ 1 |
Figure 3. The algorithm of flexible state management foreign economic activities in a multicultural region.
Source: developed and compiled by the authors.
As is shown in Figure 3, the offered algorithm envisages the initial monitoring of foreign economic activities and commodity markets (in dynamics) in the region. As a result of monitoring, foreign trade balance is determined. If the balance is positive (export exceeds import), it is necessary to determine the growth rate of the number of companies and their turnover. If the growth rate of these indicators is high (≥ 1), the region’s competitiveness is determined.
High competitiveness should be a signal for stimulation of export, low competitiveness – for stimulation of innovations. If the region’s foreign trade balance is negative or zero (import exceeds export), the growth rate of the number of companies and their turnover are determined. If the growth rate of these indicator is high (≥ 1), it is offered to limit import; if it’s low (< 1) – it is offered to stimulate import substitution in the region’s economy. Then, return to the beginning of the algorithm takes place (the algorithm is cyclic).
The approbation of the developed algorithm by the example of top-3 multicultural regions of Russia in 2018 is performed with the help of statistics that are shown in Figure 4.
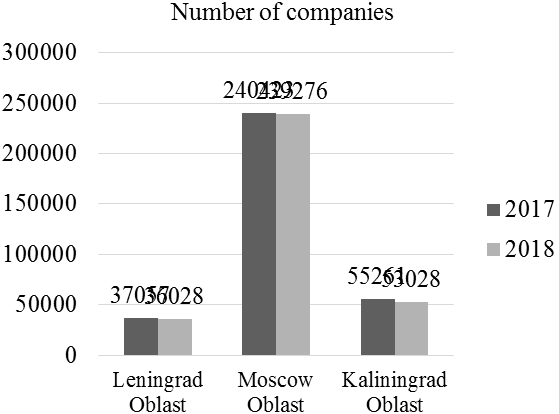
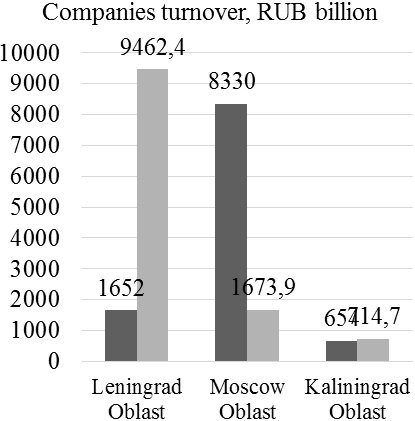
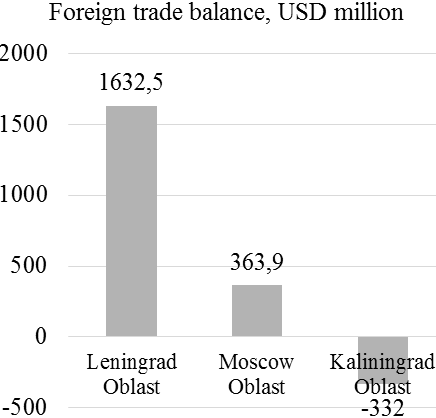
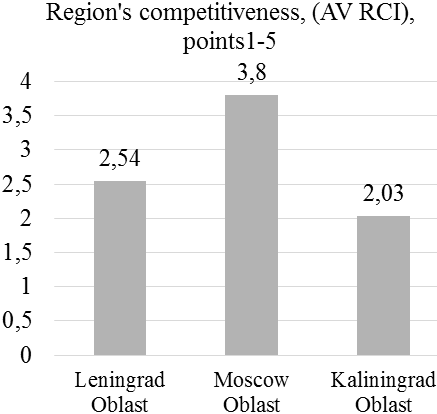
Figure 4. The results of monitoring of foreign economic activities and commodity markets (in dynamics) in top-3 multicultural regions of Russia
in 2017-2018.
Source: compiled by the authors based on Federal State Statistics Service (2019) and the Forum of Strategists – 2018: stakeholders of the future (2019).
According to Figure 4, foreign trade balance in Leningrad Oblast (USD 1, 632. 5 million) and in Moscow Oblast (USD 363. 9 million) is positive. Growth rate of the number of companies in Leningrad Oblast constitutes 0. 97 (36, 028/37, 057), in Moscow Oblast – 1. 00 (239, 276/240, 423). Growth rate of companies’ turnover in Leningrad Oblast constitutes 5. 73 (9, 462/1, 652), in Moscow Oblast – 0. 20 (1, 673. 9/8, 330). Both regions should stimulate innovations for increasing the competitiveness, which, as of 2018, constituted 2. 54 points in Leningrad Oblast and 3. 8 points in Moscow Oblast.
In Kaliningrad Oblast, foreign trade balance is negative – USD -332 million. Growth rate of the number of companies in Kaliningrad Oblast constitutes 0. 96 (53, 028/55, 261), and growth rate of companies’ turnover – 13. 09 (714. 7/654). Import substitution is recommended in this region. The implementation of the offered measure is supported by high competitiveness of Kaliningrad Oblast, which, as of 2018, constituted 2. 03 points.
The results of the performed approbation of both developed algorithms showed that monitoring of the number and structure of population (in dynamics) and the labor market and monitoring of foreign economic activities and commodity markets (in dynamics) in Russia’s multicultural regions do not require special collection of statistical data; the existing data of the official statistics and simple analysis suffice.
At the same time, the framework character of the measures of state management of economy, outlined in both algorithms, should be noted. Practical implementation of these measures envisages foundation on the accumulated experience of stimulation and restraint of migration and foreign economic activities in each multicultural region and determination – in view of this experience – of the most preferable tools of management, which should differ depending on the context.
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|