
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Formatting and Inserting Equations (Second Level Heading) (Use the Microsoft Word template style: Heading 2) or (Use Times New Roman Font: 12 pt, Bold, Centered)
Formatting and Inserting Equations (Second Level Heading) (Use the Microsoft Word template style: Heading 2) or (Use Times New Roman Font: 12 pt, Bold, Centered)
Equations should be centered with equation numbers on the right-hand side (flush right). Achieving a pleasing layout of equations can be tricky in Microsoft Word, so here are some tips. You can either:
1. Copy, paste, and edit the sample equation provided (recommended), or
2. Manually insert an equation and equation number
Copy, Paste, and Edit a Sample Equation (Third Level Heading) (Use the Microsoft Word template style: Heading 3) or (Use Times New Roman Font: 10 pt, Italic, Centered)
To use this “Old Style Equation” as a “template, ” highlight the entire line, then use cut and paste to the new location. Note that the equation number will automatically update (increment).
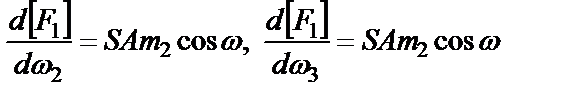 (1)(1)
(1)(1)
Manually Inserting an Equation and Equation Number (Third Level Heading) (Use the Microsoft Word template style: Heading 3) or (Use Times New Roman Font: 10 pt, Italic, Centered)
If you prefer to manually insert and number equations, follow this step-by-step guide:
1. Make sure you can see “hidden characters” by switching on “show invisibles” from the Home menu (it looks like this:  ). This allows you to see paragraph markers (¶) and tab characters (à ), which are usually hidden from view.
). This allows you to see paragraph markers (¶) and tab characters (à ), which are usually hidden from view.
2. Create a blank paragraph by pressing [ENTER].
3. Format your new blank paragraph by applying the Microsoft Word template style: Equation. The Equation paragraph style sets up the tabs so that you can center the equation and have an equation number appear at the right.
4. Place your cursor at the start of your new paragraph and press the [TAB] key twice.
5. Place your cursor between the tab characters (à ) and insert your equation using Insert ð Object ð Microsoft Equation 3. 0.
6. To add an equation number, place your cursor at the end of the paragraph (just before the paragraph markers (¶) and after the second tab character (à )).
7. On the Insert tab, in the Text group, click Quick Parts and then click Field:
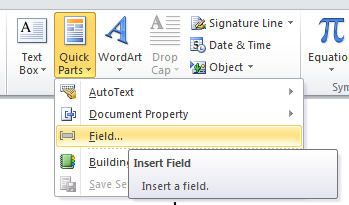
8. A dialog box should appear:
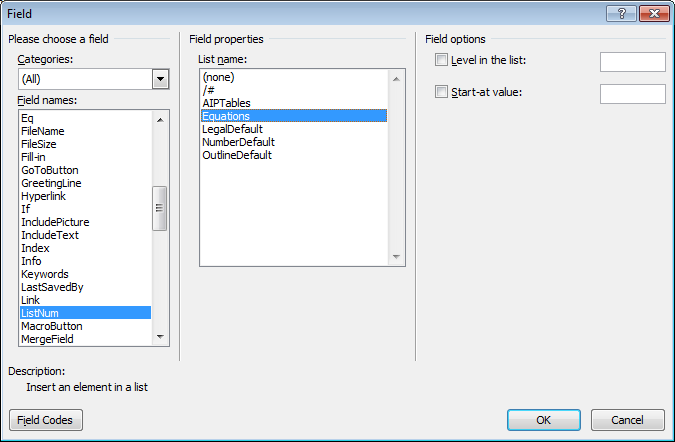
9. From the list of Field Names on the left of the dialog box, select ListNum.
10. From the list of Field properties on the right, select the “Equations” List name and click OK. You should now see an equation number in parentheses: e. g., (3).
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|