
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
ACTIVE VOCABULARY. RESPIRATION
ACTIVE VOCABULARY
Read and learn the following words and word combinations:
1. breathing дыхание
2. provide обеспечивать
3. interchange обмен
4. protective защитный
5. cage клетка
6. rib ребро
7. muscle мышца
8. diaphragm диафрагма
9. abdomen живот
10. throat горло
11. larynx глотка
12. trachea трахея
13. bronchi бронхи
14. huge огромный
15. air sac легочная альвеола
16. network сеть
17. passage проход, проходить
18. airway воздушный путь
19. surround окружать
20. simultaneously одновременно
21. replenish пополнять; снова насыщать
22. eliminate устранять
RESPIRATION
Respiration means breathing. Its function is to provide the means whereby oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves. This interchange of gases occurs in the lungs which are situated in the chest, one on each side of the heart.
The chest forms a protective cage for the heart and lungs. The bars of the cage are formed by the ribs – which are joined to the breast bone in front and spine behind. The spaces between the ribs are filled by the rib muscles. The floor of the cage is formed by the diaphragm, which is a sheet of muscle separating the chest from the abdomen.
In order to reach the lungs, the air we breathe enters the 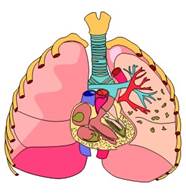 throat through the nose or mouth and passes into the larynx. Below the larynx the air passes along a tube called the trachea, which runs down the neck to the chest where it divides into two. These two branches are known as the right and left bronchi and they enter their respective lungs. Just as arteries divide up into smaller arteries and finally into thin –
throat through the nose or mouth and passes into the larynx. Below the larynx the air passes along a tube called the trachea, which runs down the neck to the chest where it divides into two. These two branches are known as the right and left bronchi and they enter their respective lungs. Just as arteries divide up into smaller arteries and finally into thin –
walled capillaries, so do the bronchi divide inside the lungs. Each bronchus divides into many smaller and smaller tubes until eventually ends up as a huge number of tiny air sacs, which comprise each lung. A network of capillaries originating from the pulmonary artery passes round each air sac.
Air breathed in through the nose passes via the throat, larynx, trachea and bronchi to the air sacs of the lungs. This passage from nose to lungs is known as the airway. In the lungs, oxygen from the air passes through the thin walls of each air sac and its surrounding capillary to reach the blood. In the same way carbon dioxide passes simultaneously out of the blood into the air sacs. This gaseous exchange for replenishing the blood with oxygen and eliminating the waste product, carbon dioxide, is the sole purpose of respiration.
Oxygen enters the blood by combining with hemoglobin in the red cells; where as carbon dioxide is carried by the plasma.
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|