
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Метод Симпсона. Код программы
Метод Симпсона
Формула выведена для п = 2, h = (b-a)/2.
Определим:
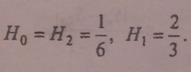
Тогда простая формула парабол имеет вид
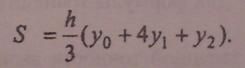
Уточненная формула парабол.
Для увеличения точности разделим интервал [я, в] на четное число n. Получим узлы x0 ,x1,…,xn , x0 = a, xn = b
Уточненная формула парабол запишется в виде
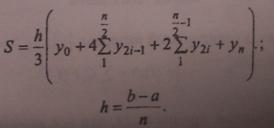
Код программы
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
double f(double x){
double y;
y=log(fabs(1-1.2*cos(x)))*cos(x)*cos(x)*cos(x);
return y;
}
double trapezium(int n, double a, double b){
double h;
double integral;
n=1000;
integral=0;
b=3.14;
a=0;
h=(b-a)/n;
integral=(f(a)+f(b));
int i;
for (i=1;i<n;i++){
integral+=2*f(a+h*i);
}
integral=integral*h/2;
return integral;
}
double simpson(int n, double a, double b){
double h;
double integral;
integral=0;
n=1000;
b=3.14;
a=0;
h=(b-a)/n;
integral=f(a)+f(b);
int i;
for (i=1;i<(n-1);i++){
if (fmod(i,2)==0){
integral+=2*f(a+h*i);
} else {
integral+=4*f(a+h*i);
}
}
integral=integral*h/3;
return integral;
}
///// pogreh ///////
double simpson2(int n, double a, double b){
double h;
double integral;
n=1000;
b=3.14;
a=0;
integral=0;
n=n/2;
h=(b-a)/n;
integral=f(a)+f(b);
int i;
for (i=1;i<(n-1);i++){
if (fmod(i,2)==0){
integral+=2*f(a+h*i);
} else {
integral+=4*f(a+h*i);
}
}
integral=integral*h/3;
return integral;
}
///////////
double chebyshev(int n, double a, double b){
double integral,t[n+1],x[n+1];
b=3.14;
a=0;
integral=0;
switch (n){
case 1:
t[0]=-0.5773;t[1]=0.5773;
break;
case 2:
t[0]=-0.7071;t[1]=0;t[2]=0.7071;
break;
case 3:
t[0]=-0.7947;t[1]=-0.1876;t[2]=0.1876;t[3]=0.7947;
break;
case 4:
t[0]=-0.8325;t[1]=-0.3746;t[2]=0;t[3]=0.3746;t[4]=0.8325;
break;
case 5:
t[0]=-0.8662;t[1]=-0.4225;t[2]=-0.2666;t[3]=0.2666;t[4]=0.4225;t[5]=0.8662;
break;
case 6:
t[0]=-0.8839;t[1]=-0.5297;t[2]=-0.3239;t[3]=0;t[4]=0.3239;t[5]=0.5297;t[6]=0.8839;
break;
case 8:
t[0]=-0.9116;t[1]=-0.6010;t[2]=-0.5288;t[3]=-0.1679;t[4]=0;t[5]=0.1679;t[6]=0.5288;t[7]=0.6010;t[8]=0.9116;
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
x[i]=(a+b)/2+(b-a)*t[i]/2;
integral+=f(x[i]);
}
integral=(b-a)*integral/(n+1);
return integral;
}
////perecet////////
double chebyshev2(int n, double a, double b){
double integral,t[n+1],x[n+1];
b=3.14/4;
a=0;
integral=0;
switch (n){
case 1:
t[0]=-0.5773;t[1]=0.5773;
break;
case 2:
t[0]=-0.7071;t[1]=0;t[2]=0.7071;
break;
case 3:
t[0]=-0.7947;t[1]=-0.1876;t[2]=0.1876;t[3]=0.7947;
break;
case 4:
t[0]=-0.8325;t[1]=-0.3746;t[2]=0;t[3]=0.3746;t[4]=0.8325;
break;
case 5:
t[0]=-0.8662;t[1]=-0.4225;t[2]=-0.2666;t[3]=0.2666;t[4]=0.4225;t[5]=0.8662;
break;
case 6:
t[0]=-0.8839;t[1]=-0.5297;t[2]=-0.3239;t[3]=0;t[4]=0.3239;t[5]=0.5297;t[6]=0.8839;
break;
case 8:
t[0]=-0.9116;t[1]=-0.6010;t[2]=-0.5288;t[3]=-0.1679;t[4]=0;t[5]=0.1679;t[6]=0.5288;t[7]=0.6010;t[8]=0.9116;
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
x[i]=(a+b)/2+(b-a)*t[i]/2;
integral+=f(x[i]);
}
integral=(b-a)*integral/(n+1);
return integral;
}
//////////////////////
////perecet3/////
double chebyshev3(int n, double a, double b){
double integral,t[n+1],x[n+1];
b=3.14/2;
a=3.14/4;
integral=0;
switch (n){
case 1:
t[0]=-0.5773;t[1]=0.5773;
break;
case 2:
t[0]=-0.7071;t[1]=0;t[2]=0.7071;
break;
case 3:
t[0]=-0.7947;t[1]=-0.1876;t[2]=0.1876;t[3]=0.7947;
break;
case 4:
t[0]=-0.8325;t[1]=-0.3746;t[2]=0;t[3]=0.3746;t[4]=0.8325;
break;
case 5:
t[0]=-0.8662;t[1]=-0.4225;t[2]=-0.2666;t[3]=0.2666;t[4]=0.4225;t[5]=0.8662;
break;
case 6:
t[0]=-0.8839;t[1]=-0.5297;t[2]=-0.3239;t[3]=0;t[4]=0.3239;t[5]=0.5297;t[6]=0.8839;
break;
case 8:
t[0]=-0.9116;t[1]=-0.6010;t[2]=-0.5288;t[3]=-0.1679;t[4]=0;t[5]=0.1679;t[6]=0.5288;t[7]=0.6010;t[8]=0.9116;
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
x[i]=(a+b)/2+(b-a)*t[i]/2;
integral+=f(x[i]);
}
integral=(b-a)*integral/(n+1);
return integral;
}
//////////////////////
////perecet3/////
double chebyshev4(int n, double a, double b){
double integral,t[n+1],x[n+1];
b=3*3.14/4;
a=3.14/2;
integral=0;
switch (n){
case 1:
t[0]=-0.5773;t[1]=0.5773;
break;
case 2:
t[0]=-0.7071;t[1]=0;t[2]=0.7071;
break;
case 3:
t[0]=-0.7947;t[1]=-0.1876;t[2]=0.1876;t[3]=0.7947;
break;
case 4:
t[0]=-0.8325;t[1]=-0.3746;t[2]=0;t[3]=0.3746;t[4]=0.8325;
break;
case 5:
t[0]=-0.8662;t[1]=-0.4225;t[2]=-0.2666;t[3]=0.2666;t[4]=0.4225;t[5]=0.8662;
break;
case 6:
t[0]=-0.8839;t[1]=-0.5297;t[2]=-0.3239;t[3]=0;t[4]=0.3239;t[5]=0.5297;t[6]=0.8839;
break;
case 8:
t[0]=-0.9116;t[1]=-0.6010;t[2]=-0.5288;t[3]=-0.1679;t[4]=0;t[5]=0.1679;t[6]=0.5288;t[7]=0.6010;t[8]=0.9116;
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
x[i]=(a+b)/2+(b-a)*t[i]/2;
integral+=f(x[i]);
}
integral=(b-a)*integral/(n+1);
return integral;
}
//////////////////////
////perecet3/////
double chebyshev5(int n, double a, double b){
double integral,t[n+1],x[n+1];
b=3.14;
a=3*3.14/4;
integral=0;
switch (n){
case 1:
t[0]=-0.5773;t[1]=0.5773;
break;
case 2:
t[0]=-0.7071;t[1]=0;t[2]=0.7071;
break;
case 3:
t[0]=-0.7947;t[1]=-0.1876;t[2]=0.1876;t[3]=0.7947;
break;
case 4:
t[0]=-0.8325;t[1]=-0.3746;t[2]=0;t[3]=0.3746;t[4]=0.8325;
break;
case 5:
t[0]=-0.8662;t[1]=-0.4225;t[2]=-0.2666;t[3]=0.2666;t[4]=0.4225;t[5]=0.8662;
break;
case 6:
t[0]=-0.8839;t[1]=-0.5297;t[2]=-0.3239;t[3]=0;t[4]=0.3239;t[5]=0.5297;t[6]=0.8839;
break;
case 8:
t[0]=-0.9116;t[1]=-0.6010;t[2]=-0.5288;t[3]=-0.1679;t[4]=0;t[5]=0.1679;t[6]=0.5288;t[7]=0.6010;t[8]=0.9116;
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
x[i]=(a+b)/2+(b-a)*t[i]/2;
integral+=f(x[i]);
}
integral=(b-a)*integral/(n+1);
return integral;
}
//////////////////////
double gauss(int n, double a, double b){
n=5;
double integral,t[n+1],x[n+1],c[n+1];
integral=0;
switch (n){
case 1:
t[0]=-0.5773;t[1]=0.5773;
c[0]=1;c[1]=1;
break;
case 2:
t[0]=-0.7746;t[1]=0;t[2]=0.7746;
c[0]=5/9;c[1]=8/9;c[2]=5/9;
break;
case 3:
t[0]=-0.8611;t[1]=-0.3400;t[2]=0.3400;t[3]=0.8611;
c[0]=0.3479;c[1]=0.6521;c[2]=0.6521;c[3]=0.3479;
break;
case 4:
t[0]=-0.9062;t[1]=-0.5385;t[2]=0;t[3]=0.5385;t[4]=0.9062;
c[0]=0.2369;c[1]=0.4786;c[2]=512/900;c[3]=0.4786;c[4]=0.2369;
break;
case 5:
t[0]=-0.9325;t[1]=-0.6612;t[2]=-0.2386;t[3]=0.2386;t[4]=0.6612;t[5]=0.9325;
c[0]=0.1713;c[1]=0.3608;c[2]=0.4671;c[3]=0.4671;c[4]=0.3608;c[5]=0.1713;
break;
}
b=3.14;
a=0;
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
x[i]=(a+b)/2+(b-a)*t[i]/2;
integral+=f(x[i])*c[i];
}
integral=(b-a)*integral/2;
return integral;
}
int main()
{
int n,k;
n=8;
{
//cout << " trapezium = " <<trapezium(n,0,1) << endl;
cout << " simpson = " <<simpson(n,0,1) << endl;
cout << " chebyshev = " << chebyshev(n,0,1) << endl;
//cout << " gauss = " << gauss(n,0,1) << endl << endl <<endl;
}
cout << " simpson 2h = " <<simpson2(n,0,1) << endl; //n=20
cout << "chebyshev 4 int = " <<chebyshev2(n,0,1)+chebyshev3(n,0,1)+chebyshev4(n,0,1)+chebyshev5(n,0,1) << endl << endl; //n=6
float e;
//e=fabs((simpson(n,0,1)-simpson2(n,0,1))/15);
switch (n){
case 1:
k=4;//4
break;
case 2:
k=4;//4
break;
case 3:
k=6;//6
break;
case 4:
k=6;//6
break;
case 5:
k=8;
break;
case 6:
k=8;
break;
case 8:
k=10;//10
break;
}
e=fabs((chebyshev(n,0,1)-chebyshev2(n,0,1)-chebyshev3(n,0,1)-chebyshev4(n,0,1)-chebyshev5(n,0,1))/((pow(2,k)-1)));
cout << " RC = ";//<<e<<endl;
printf("%10.8f ", e);
e=fabs(simpson(n,0,1)-simpson2(n,0,1))/15;
cout << " RS = ";//<<e<<endl;
printf("%10.8f ", e);
getch();
}
Результат
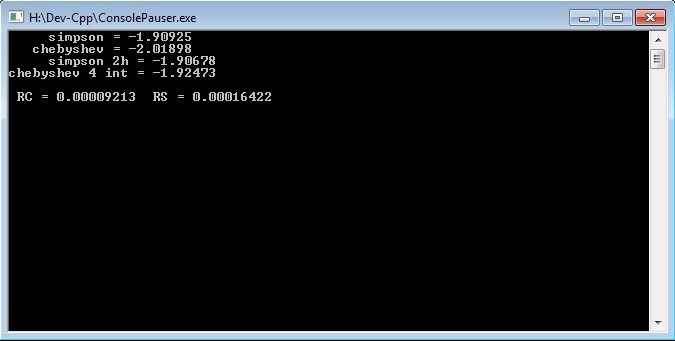
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|