
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Cortical granules contain enzymes and glycosaminoglycans. They will be needed during fertilization to prevent polyspermia.
Cortical granules contain enzymes and glycosaminoglycans. They will be needed during fertilization to prevent polyspermia.

STAGES OF EMBRYONAL DEVELOPMENT:
1. Fertilization 2. Cleavage 3. Gastrulation 4. Histogenesis (tissue development) 5 Organogenesis (organ development) and system genesis (formation of organ systems).
Fertilization is the fusion of male and female germ cells, as a result of which the diploid set of chromosomes is restored and a unicellular zygote embryo appears.
Fertilization includes three phases:
1. Distant interaction
2. Contact of gametes
3. Penetration
With distant interaction there is a movement of the sperm in the direction of the ovum. This is due to the movements of the tail, chemotaxis (the movement of the sperm to substances that are secreted by the ovum and attract the sperm to it. These substances are called gynogamones) and rheotaxis (the ability of the sperm to move against the flow of fluid in the female genital tract).
Simultaneously with the movements of the sperm, capacitation is the acquisition of the fertilizing ability by the sperm. At the same time masking proteins are removed from the sperm receptor, which close the receptor and prevent it from recognizing the ovum.
Further, contact interaction begins - when the sperm reaches the female reproductive cell and begins to rotate it. In this case, an acrosome reaction occurs - the release of enzymes from the acrosome. Enzymes begin to destroy the shell of the ovum - first the follicular cells, and then the corona radiata. The female reproductive cell loses these two outer membranes and becomes naked. The process of destruction of the oocyte membranes is called denudation. The transparent zone is destroyed only in the place where the first sperm penetrated.
Next, the third phase of fertilization begins - penetration. Here the sperm head is pulled into the ovum. The nuclei of the sperm and ovum are transformed into the male and female pronuclei and fused together and form zygote.
Here, a cortical reaction occurs - this is the release of the contents of the cortical granules. Enzymes from these granules destroy the test connection between the ovolemma and the zonapellucida, as a result of which a narrow slit-like space is formed between them - the perivitelline space. Glycosaminoglycans from granules bind to the water of the perivitelline space and it becomes hard and forms a fertilization membrane - it prevents polyspermia in humans. Further, a zone reaction occurs - when ZP3 is modified. Changes its structure and ceases to be a receptor for sperm. This is the second defense against polysperimia in humans.
Cleavage is a series of successive mitotic divisions of the zygote resulting in the formation of a blastula.
Cleavage differs from mitosis by the absence of the G1 interphase period, i. e. there is no growth of daughter cells and they do not reach the size of the mother. With each division the daughter cells (blastomeres) become smaller and smaller during cleavage.
In humans cleavage: complete (holoblastic)
unequal
asynchronous
The complete type of cleavage means that all the material of the zygote is devides. This happens when there is a small amount of yolk in the ovum. If there is a lot of yolk in the ovum then this type of female sex cell will lead to the fact that the resulting zygote will not split completely. Only the material of the animal (yolk-free) pole will be crushed. And the material of the vegetative pole will not split at all, since it contains a heavy yolk that interferes with division.
Unequal cleavage means that yolk-free zygote material will divide at a faster rate than yolk-containing material. Therefore, as a result, the blastula will consist of small cells (microblastomeres) - this is a material without yolk and large cells (macroblastomeres) - this is the part of the zygote that contained the yolk.
Synchronous cleavage is the appearance of a multiple number of blastomeres (2, 4, 8, 16, 32). This happens when cells devide at the same rate.
in humans, cleavage is asynchronous - when a multiple number of blastomeres appears (2. 3 5. 8, etc. ) due to different cleavage rates of blastomeres).
In humans, a blastula is called a blastocyst .
The blastocyst consists of:
- The outer cell mass (trophoblast) is small light-colored cells or microblastomeres. It starts the chorion and placenta.
- Inner cell mass (embryoblast ) - these are large and dark cells or macroblastomeres). From it, the embryo develops, as well as the amnion and yolk sac.
- Blastocel is a cavity filled with fluid.
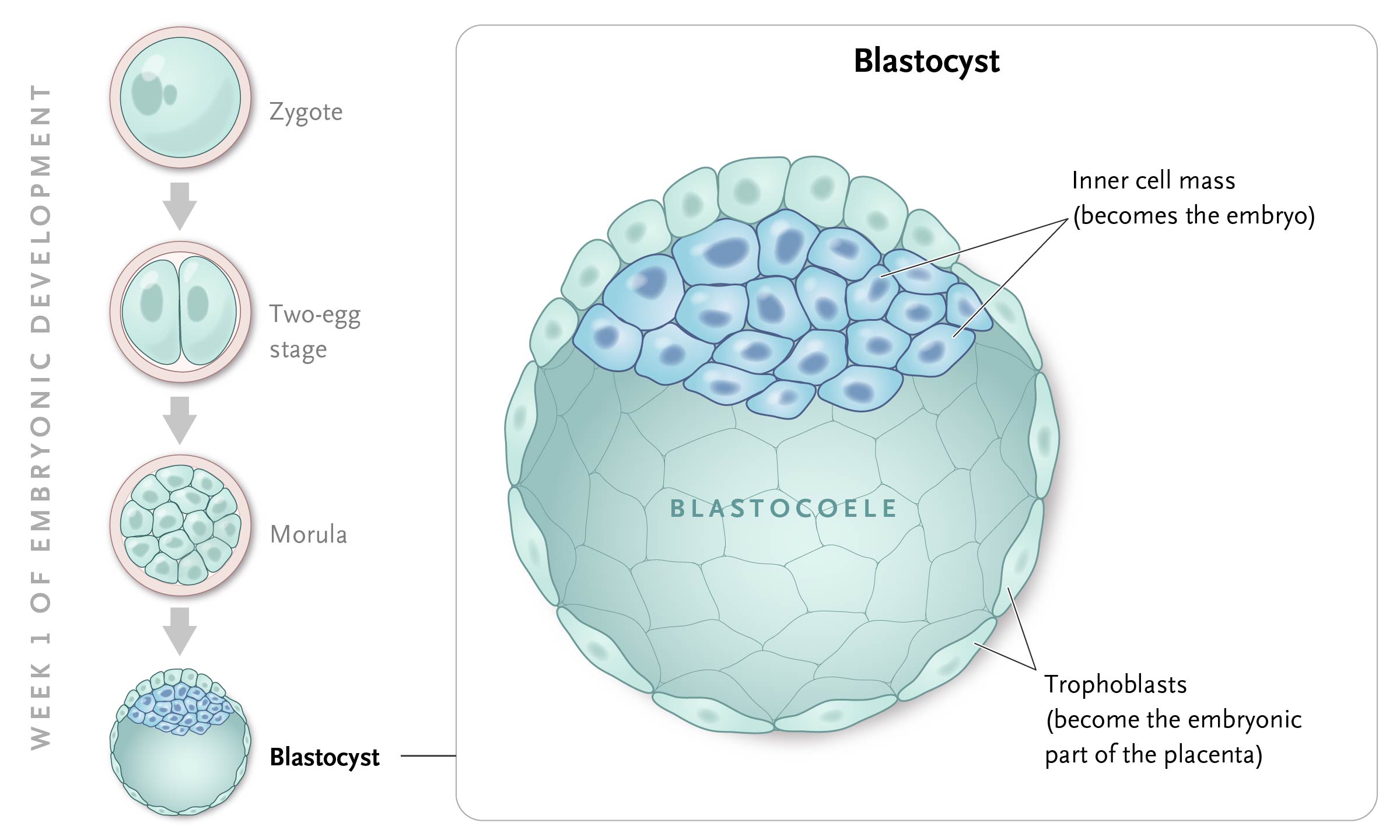
Process of cleavage: 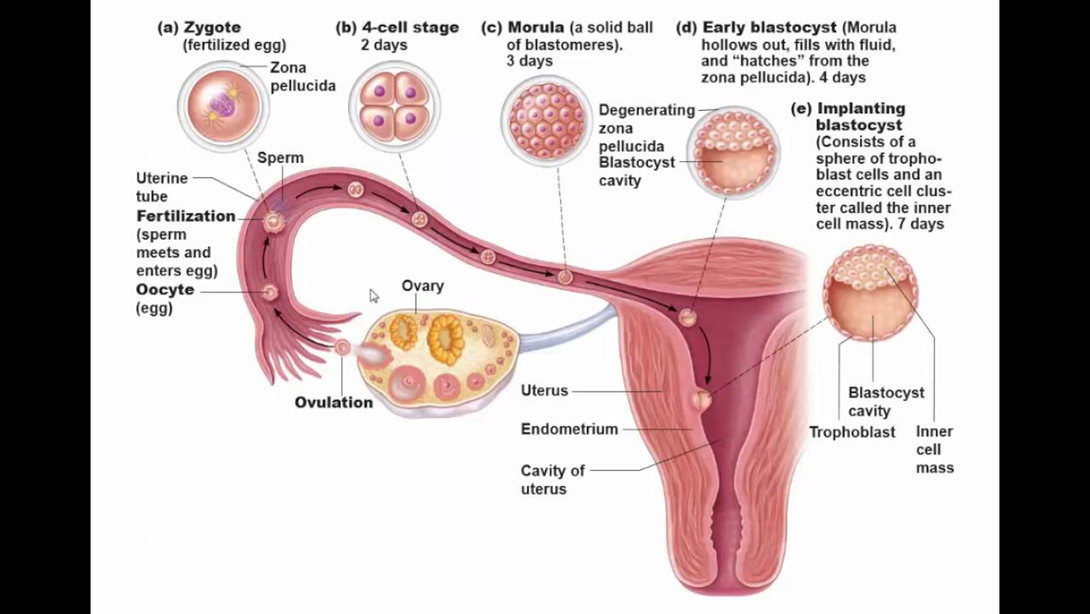
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|