
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Digestion 1. General Principles of Gastrointestinal Motility
Digestion 1
General Principles of Gastrointestinal Motility
The goal of lesson is studying of motility function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Questions for discussion
1. General Principles of Gastrointestinal Motility
2. Motor acts of the mouth: chewing, swallowing, their regulation.
3. Digestion in the stomach, movement. Regulation of this process.
4. Digestion in the small intestine. Movement, its regulation.
5. Movement of the colon, its regulation.
Books recommended
1. Ganong W. F. Review of Medical Physiology. 20thed; McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001. – P.
2. Guyton A. C., Hall J. E. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12thed; WB Saunders, 2008.
Practical work 1. Recording and analysis of the masticaciogram in humans when chewing food products of varying degrees of hardness.
For this work you need: masticaciograph, a set of food products (bread, rusk, dragee, apple, etc. ).
Technique. The sensor of the masticaciograph, consisting of a rubber cuff enclosed in a flexible inextensible case, fix it on the lower jaw of the volunteer, then connect it to the recording device. Set the calibration of the instrument. Record several cycles of masticatory movements of the lower jaw (masticaciogram) when eating food of varying degrees of hardness: bread, breadcrumb, dragee, apple, etc. Use the recorded masticaciograms to analyze the duration of the phases, amplitude and frequency of chewing during the main chewing phase when chewing products of different hardness.
Results. Draw 2 masticaciograms: when chewing soft and hard products. Point the phases.
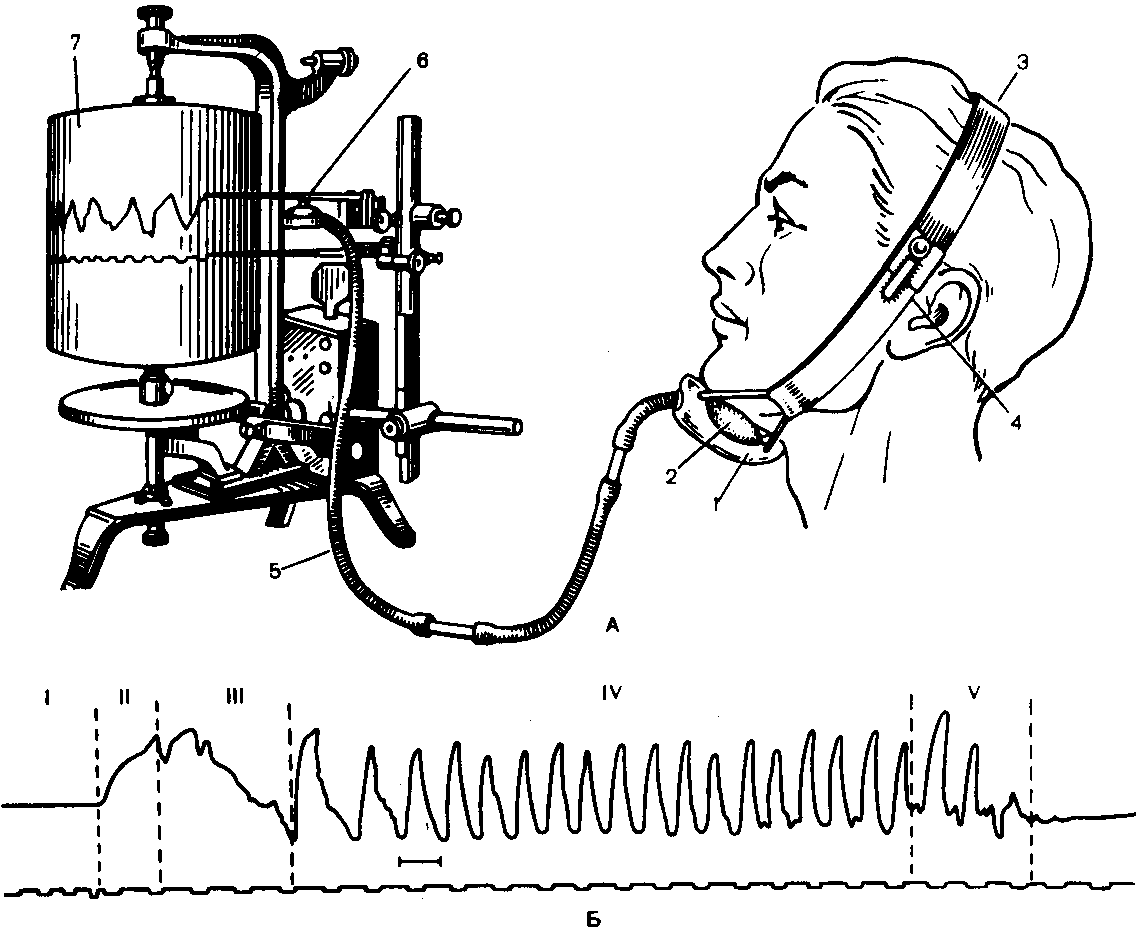
Normal chewing phase consists of the following phases: 1 - rest phase, 2 – intake of food in the mouth, 3 - indicative chewing phase, 4 - the main phase of chewing, 5 - the formation of the food lump and the beginning of its ingestion. Calculate the duration of the phases, the number of masticatory movements in the main phase while taking food products of different hardness.
Conclusions. Indicate what the mechanism of the act of chewing, why the amplitude of chewing and the duration of the phases when chewing different products.
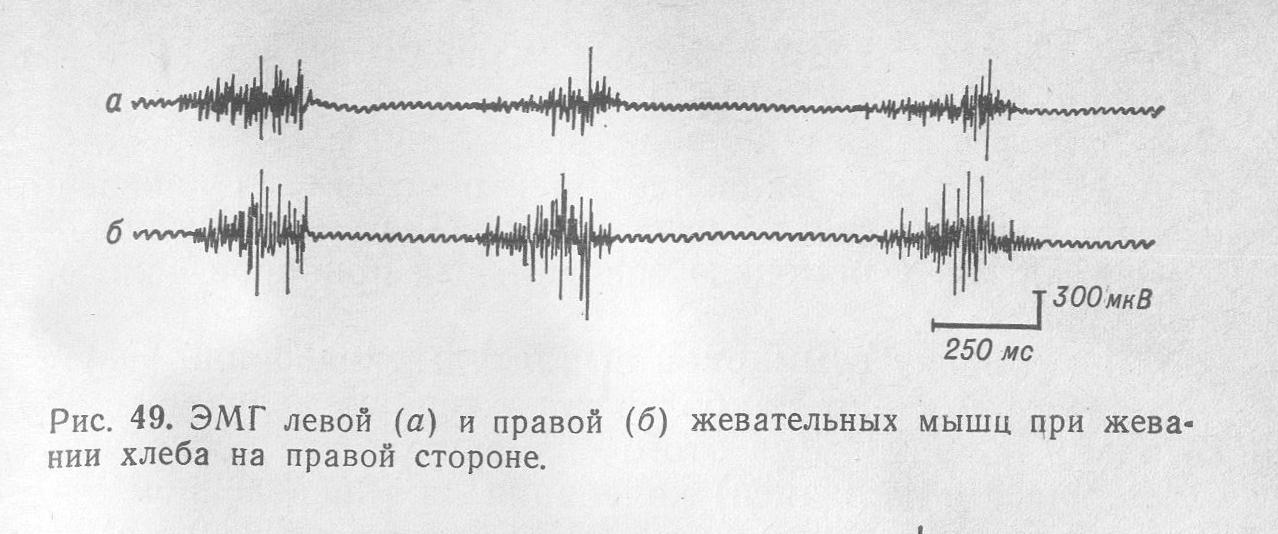
Practical work 2. Electromyogram of masticatory muscles recorded for different types of activities.
For this work you need: electromyography, electrodes.
Technique. Electrodes placed on the skin in the area projection of the main masticatory muscles, the EMG record.
Result: to compare the EMG with the continuous tension of the masticatory muscles, when making chewing movements.
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|