
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ РК
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ РК
КАЗАХСКАЯ ГОЛОВНАЯЙ АРХИТЕКТУРНО-СТРОИТЕЛЬНАЯ АКАДЕМИЯ
Учебный год___2017-2018____
ПАСПОРТ
ТЕСТОВЫХ ЗАДАНИЙ
Форма контроля ______летняя__________________________________________________
(зимняя/летняя экзаменационная сессия по формам обучения/комплекный государственный экзамен по специальности/государственный экзамен по профильным дисциплинам/экзамен/ сессии выпускного курса/экзамен/сессия по практике/входной срез/государственный срез по специальности)
Дисциплина: ____________BuildingConstruction 1 _____________
Специальность: ____Строительство, Архитектура___________________
Группы: _____Cтр-16-13**, Арх-15-8**_____________________
Параметры теста:
Форма и язык обучения_______английский________
Количество кредитов/вопросов_____240_______
Утверждено на заседании __________________________
Протокол № 1 от _______________________________
Председатель МС Джумадилова С. Ж ______________________________
(ФИО) (подпись, дата)
Декан ФОС Полякова И. М. _______________________________
(ФИО) (подпись, дата)
Академический/ассоциир/профессор по направлению специальности дисциплины:
____________________________________ ______________________________________
(ФИО) (подпись, дата)
____________________________________ ___________________________________________________
(ФИО) (подпись, дата)
Регистратор Буганова С. Н. _______________________________
(ФИО) ( подпись, дата)
Разработчик Козюкова Н. В. _______________________________
(ФИО) (подпись, дата)
$$$ 1 Principle of reinforced concrete?
$$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and steel reinforcement, rationally located in the structures for the perception of tensile and, in some cases, and compression forces;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement, located arbitrarily in the cross section of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement that is located only in compressed zones of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement placed in the centre of gravity of the cross section of the element.
$$$ 2 Factors ensuring the joint operation of concrete and reinforcement?
$$ similar to those of the coefficients of linear expansion, of grip between concrete and reinforcement, protecting the reinforcement against corrosion and other external influences;
$ shrinkage and creep of concrete, the adhesion of concrete with reinforcement, protection of reinforcement against mechanical impact;
$ use of reinforcement periodic profile, the compression of the reinforcement due to shrinkage, the same coefficients of linear expansion;
$ protection of the reinforcement from external influences (corrosion, high temperature, mechanical), high strength concrete in compression, low strength of concrete in tension.
$$$ 3 How depends the strength of concrete from time to time?
$$ under favorable conditions the strength of concrete increases;
$ increases whatever the conditions;
$ the strength of concrete is reduced;
$ the strength of concrete does not change over time.
$$$ 4 Effect on concrete strength of stress?
$$ strength of concrete in compression is greater than in tension;
$ the strength of concrete in tension more than in compression;
$ the strength of concrete is the same in compression and in tension;
$ the strength of concrete are the same for dense concrete.
$$$ 5 What is called the class of concrete strength?
$$ temporary compressive strength of concrete cubes with size 150 mm rib, tested after 28 days of storage at a temperature of температуре 20 ± 20С With the statistical variability;
$ temporary resistance to axial compression of concrete prisms at the age of 28 days;
$ average value of tensile concrete compression test cubes standard;
$ temporary resistance to axial tension specimens at age of 28 days, taking into account statistical variability.
$$$ 6 What is shrinkage of concrete?
$$ the decrease in the volume of concrete hardening in air;
$ the decrease in hardening in water;
$ the decrease at high temperatures;
$ the increase of volume during solidification in the water.
$$$ 7 What is called creep of concrete?
$$ the increase in inelastic strain with time at constant stress;
$ the decrease in deformation of the loaded specimen over time;
$ the increase in the elastic deformation under the influence of long-acting load;
$ increase in deformation under load over time.
$$$ 8 Yield strength of steel?
$$ stress at which strain increases without load change;
$ stress up to which the material acts elastically;
$ stress at which permanent deformation amount to 0. 02%;
$ stress at which there is a gap element.
$$$ 9 What distinguishes prism strength from cube?
$$ less;
$ equal;
$ more;
$ are equal if the height of the prism is 2 times the height of the cube.
$$$ 10 What is the difference between strength of concrete tensile strength of concrete in compression?
$$ less;
$ more;
$ equal;
$ less only for lightweight concrete.
$$$ 11 What class is a plain reinforcement?
$$ A-I;
$ A-II;
$ A-III;
$ A-IV.
$$$ 12 What are the signs classified reinforcements?
$$ strength and deformability;
$ the chemical composition;
$ deformability;
$ strength.
$$$ 13 Specify the class of hot rolled reinforcement periodic profile?
$$ А-II…А-VI;
$ А-I;
$ Вр-I;
$ Вр-II.
$$$ 14 Specify the class of cold-drawn wire reinforcement with periodic profile?
$$ Вр-I, Вр-II;
$ А-III, А-IV;
$ A-I, A-II;
$ В-II.
$$$ 15 Specify the class of reinforcement cold-drawn plain profile?
$$ В-II;
$ Ат-IV, Ат-V;
$ Вр-I, Вр-II
$ A-I, А-III.
$$$ 16 For what purpose on the surface of the reinforcement creates a different kind of profile (ridges, bumps, etc. )?
$$ to improve the adhesion of the reinforcement with the concrete;
$ to improve the strength properties;
$ saving;
$ to improve weldability.
$$$ 17 Purpose of the thickness of the protective layer.
$$ enable collaboration reinforcement with concrete and to protect reinforcement from corrosion, high temperatures, mechanical damage;
$ to protect the reinforcement from corrosion;
$ to protect the reinforcement from mechanical damage;
$ protect the reinforcements from sudden changes of temperature.
$$$ 18 Goal of creating a prestressed reinforced concrete?
$$ to improve the crack resistance and stiffness, to ensure the use of high-strength reinforcement;
$ increase the carrying capacity of the element;
$ to increase the toughness and reduce the shrinkage strain;
$ to increase the strength of concrete.
$$$ 19 What characterizes the end of the first stage of stress-strain state of bending?
$$ stress in concrete stretched zone reached the ultimate strength (Rbt), in the compressed zone sb< Rb, linear diagram;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and stretched zones are changed according to the linear law (triangular diagram);
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone sb< Rb, in the tensile zone cracks;
$ the stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb=Rb) in the tensile zone is equal to the tensile strength (sbt=Rbt).
$$$ 20 The second stage is characterized by the stress-strain state of bending…
$$ in the tensile zone of concrete cracks. At cracked sections, the stress in the tensile reinforcement area is perceived. ((ss - Rs) Stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curvilinear;
$ stress in concrete is compressed and stretched zones is less than the limit, diagram the stresses in the tensile zone of curvilinear;
$ stress in concrete is compressed and stretched zones is less than the limit, a linear diagram;
$ stress in the tensile reinforcement in the cross section with a crack has reached the limit values (ss = Rs), stresses in the concrete compressed zone is equal to the tensile strength (sb=Rb), linear diagram.
$$$ 21 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state are used to calculate the strength?
$$ third;
$ second;
$ first;
$ I-a.
$$$ 22 What characterizes the third stage of the stress-strain state of bending?
$$ stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb = Rb), curvilinear stress diagram, the stress in the reinforcement is stretched zone has reached the physical or conditional yield strength;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is linear, the tension in the stretched zone reinforcement is less than yield stress;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit ((sb< Rb), the diagram is curved, the tension in the stretched zone reinforcement equals the yield stress.
$$$ 23 Main methods of creating pre-stress in the reinforcement?
$$ mechanical, electrothermomechanical, electrothermal;
$ electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermomechanical, mechanical;
$ mechanical, electrothermal.
$$$ 24 How to create pre-stressed concrete?
$$ tension reinforcement in abutments and concrete;
$ tension reinforcement to the concrete previously fabricated structures;
$ tension reinforcement at abutments with the subsequent concreting;
$ tension reinforcement with the help of winding machines.
$$$ 25 How changes the stress state of the reinforcement in the precast structures over time?
$$ reduces;
$ does not change;
$ increases;
$ change depends on initial stress values.
$$$ 26 What stress loss in the reinforcement occur before and during concrete prestressing under tension to the concrete?
$$ 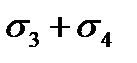 ;
;
$ 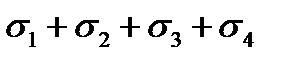 ;
;
$ 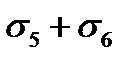 ;
;
$ 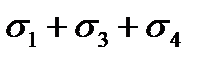 .
.
$$$ 27 What stress loss in the reinforcement occurs after prestressing of the concrete during pretensioning?
$$ 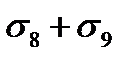 ;
;
$ 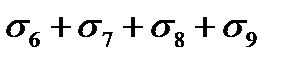 ;
;
$ 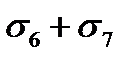 ;
;
$ 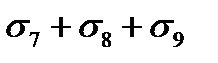 .
.
$$$ 28 What stress loss in the reinforcement occurs before and after prestressing of the concrete during pretensioning?
$$ 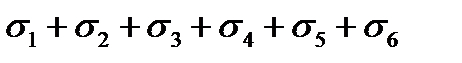 ;
;
$ 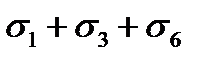 ;
;
$ 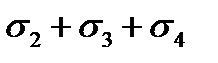 ;
;
$ 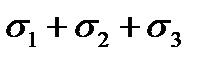 .
.
$$$ 29 What the stress loss in the reinforcement occur after the compression of the concrete in tension to the concrete?
$$ 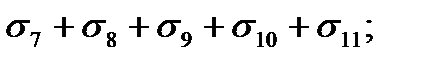
$ 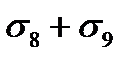 ;
;
$ 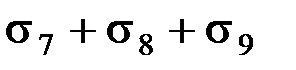 ;
;
$ 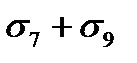 .
.
$$$ 30 Purpose of the calculation of the ultimate limit state of the first group?
$$ to prevent any (brittle, ductile, fatigue) fracture, buckling shape and position;
$ to prevent the development of deformities and displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape or position;
$ to prevent brittle fracture.
$$$ 31 Purpose of the calculation of the ultimate limit state of the second group?
$$ to prevent excessive opening of cracks, excessive movement;
$ to prevent structural failure from any external influence;
$ to prevent the development of excessive displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape and position.
$$$ 32 Classification of loads?
$$ dead and live;
$ dead and long-term;
$ long-term and short-term;
$ dead, live and special.
$$$ 33 Classification of live loads?
$$ long, short and special;
$ dead and long-term;
$ dead, live and special;
$ long-term and short-term.
$$$ 34 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state is used to calculate the cracking?
$$ first;
$ second;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 35 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state is used to calculate the crack width and deformation?
$$ second;
$ first;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 36 What is the purpose of introducing the partial safety factor for load?
$$ to account for variability of loads;
$ to account for the nature of the impact loads on the structure;
$ to account for the magnitude of loads;
$ to identify the loads class.
$$$ 37 What are the possible changes of the safety factor on the load gf?
$$ can be greater than 1, can be less than 0;
$ less than 1;
$ equals 1;
$ greater than 1.
$$$ 38 Design loads?
$$ establish multiplying the normative load by the safety factor q = qn g f;
$ set at their nominal values;
$ set norms with a given probability of exceedance;
$ establish dividing of the normative load by the safety factor 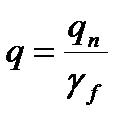 ;
;
$$$ 39 How are classified live loads?
$$ long-term, short-term and special;
$ short-term and special;
$ long-term and special;
$ short-term and long-term.
$$$ 40 What loads are in the main combinations?
$$ dead, long-term and short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ dead and long-term;
$ dead.
$$$ 41 Which loads are included in the special combinations?
$$ dead, long-term and possible short-term and one of the specials;
$ long-term and possible short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ short-term and special.
$$$ 42 According to what limit state group calculation the design resistance is equal to normative?
$$ the second group of limit states;
$ the first group of limit states;
$ in the calculation of strength;
$ when calculating the deformations.
$$$ 43 To which is introduced a boundary height of the compressed zone in bending?
$$ to clarify on what condition works the section (on the case I or case II of the third stage);
$ to ensure the strength of the element in the compressed zone;
$ to ensure the strength of the element in the tensile zone;
$ to ensure the strength of the element on both zones.
$$$ 44 Purpose of transverse reinforcement in bending elements?
$$ for the perception of the principal tensile stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of main compressive stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of tangential stresses;
$ for the perception of tensile stresses normal to the sections.
$$$ 45 Purpose of the longitudinal reinforcement in bending elements?
$$ for perception mainly tensile stresses and, in some cases, compressive in the normal section;
$ for the perception of compressive stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of the principal tensile stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of shear stresses.
$$$ 46 In some cases, resort to the installation of double reinforcements?
$$ low strength of concrete in compressed zone;
$ insufficient strength of concrete in tension zone;
$ low strength of tension reinforcement;
$ insufficient area of tension reinforcement.
$$$ 47 Which strength conditions at bending for rectangular section is correct 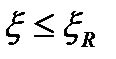 ?
?
$$ 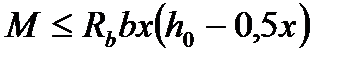 ;
;
$ 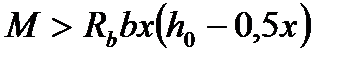 ;
;
$ 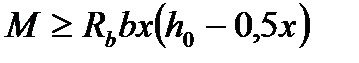 ;
;
$ 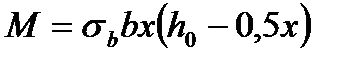 .
.
$$$ 48 What are the constructive requirements, ensuring the strength of the inclined sections on bending moment?
$$ longitudinal tension reinforcement should be brought to the supports, and ensures its reliable anchoring;
$ part of the longitudinal tensile reinforcement should be brought to the supports, and ensures its reliable anchoring;
$ longitudinal tension reinforcement should be brought to the supports;
$ part of the longitudinal reinforcement should be brought to the supports, additional transverse reinforcement is placed.
$$$ 49 Under what conditions is provided the strength of the inclined sections to the action of bending moment?
$$ 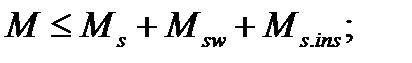
$ 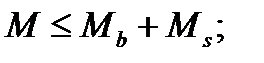
$ 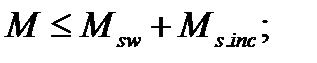
$ 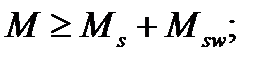
$$$ 50 Under what conditions is provided the strength of the inclined sections to the action of shear force?
$$ 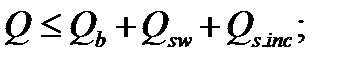
$ 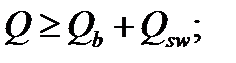
$ 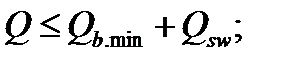
$ 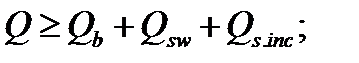
$$$ 51 Reasons that cause the formation of inclined cracks?
$$ main tensile stresses;
$ stresses perpendicular to the rod axis (y);
$ stresses in the direction of axes x and y;
$ stresses along the axis of the rod (x).
$$$ 52 Specify the correct dependency in determining the reinforcement ratio of bending elements.
$$ 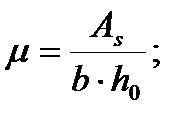
$ 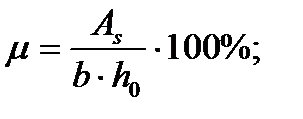
$ 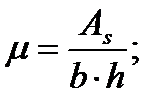
$ 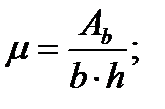
$$$ 53 What kind of structures are assigned grade of concrete on frost resistance?
$$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of alternate freezing and thawing;
$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ for all;
$ requirements of thermal insulation.
$$$ 54 What kind of structures are assigned grade of concrete on water resistance?
$$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of the transverse freezing and thawing;
$ requirements insulation;
$ for self-stressed frames
$$$ 55 What kind of structures in the project is specified the class of concrete on strength under axial compression?
$$ for all;
$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of alternate freezing and thawing;
$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ requirements of thermal insulation.
$$$ 56 In which cases are assigned the class of concrete strength on axial tension?
$$ when this feature will be essential and controlled at the production;
$ for all;
$ requirements insulation;
$ requirements limitations permeability.
$$$ 57 Design resistance of the transverse reinforcement (stirrups, bent bars) is reduced compared to Rs regardless of the type and class of reinforcement on the coefficient of working conditions, equals to:
$$ 0. 8
$ 0. 9
$ 0. 85
$ 0. 95
$$$ 58 When in the bent element arise inclined cracks near the supports?
$$ 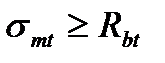
$ 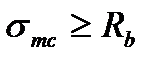
$ 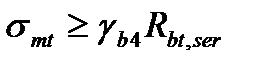
$ 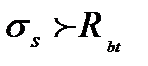
$$$ 59 For the strength of the concrete element along an inclined compressed strip between the inclined cracks must be performed the condition
$$ 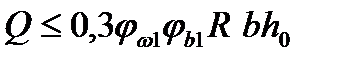
$ 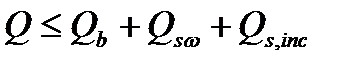
$ 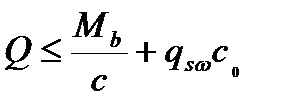
$ 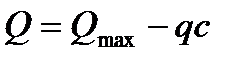
$$$ 60 Calculation of strength of reinforced concrete elements for inclined crack at the action of the transverse forces produced by the formula
$$ 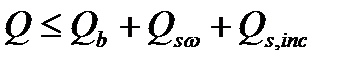
$ 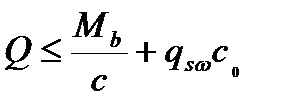
$ 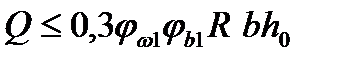
$ 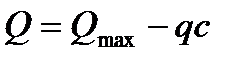
$$$ 61 Most rational shape of cross sections of bent prestressed elements is
$$ square
$ rectangular
$ I-shaped
$ trapezoid
$$$ 62 Definition of concrete?
$$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and steel reinforcement, rationally located in the structures for the perception of tensile and, in some cases, and compression forces;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement, located arbitrarily in the cross section of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement that is located only in compressed zones of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement placed in the centre of gravity of the cross section of the element.
$$$ 63 How the joint work of concrete and reinforcement is provided?
$$ similar to those of the coefficients of linear expansion, of the grip between reinforcement and concrete, protecting the reinforcement against corrosion and other external influences;
$ shrinkage and creep of concrete, the adhesion of concrete with reinforcement, protection of reinforcement against mechanical impacts;
$ use of reinforcement periodic profile, the compression of the reinforcement due to shrinkage, the same coefficients of linear expansion;
$ protection of the reinforcement from external influences (corrosion, high temperature, mechanical), high strength concrete in compression, low strength of concrete in tension.
$$$ 64 Class of concrete on strength?
$$ temporary compressive strength of concrete cubes with size 150 mm, tested after 28 days of storage at a temperature of 20 ± 2 °С including the statistical variability;
$ temporary resistance to axial compression of concrete prisms at the age of 28 days;
$ average value of tensile concrete compression test cubes standard;
$ temporary resistance to axial tension specimens at age of 28 days, taking into account statistical variability.
$$$ 65 Classification of reinforcements?
$$ strength and deformability;
$ chemical composition;
$ deformability;
$ strength.
$$$ 66 Specify the class of a plain reinforcement?
$$ A-I;
$ A-II;
$ A-III;
$ A-IV.
$$$ 67 Describe the end of the first stage of stress-strain state at bending?
$$ stress in concrete of tension zone reached the ultimate strength (Rbt), in the compressed zone sb< Rb, linear diagram;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and stretched zones are changed according to the linear law (triangular diagram);
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone sb< Rb, in the tensile zone cracks;
$ the stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb = Rb) in the tensile zone is equal to the tensile strength (sbt = Rbt).
$$$ 68 What for the different profiles on the surface of the reinforcement (ribs, bumps, etc. ) are created?
$$ to improve the adhesion of the reinforcement with the concrete;
$ to improve the strength properties;
$ to improve the deformation properties;
$ to improve weldability.
$$$ 69 Describe the third stage of the stress-strain state at bending?
$$ stress in the concrete of compressed zone equal to the ultimate (sb = Rb), curvilinear stress diagram, the stress in the reinforcement of tension zone has reached the physical or conditional yield strength;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is linear, the stress in the stretched zone reinforcement is less than yield stress;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curved, the stress in the reinforcement of tension zone equals the yield stress.
$$$ 70 Describe the second stage of the stress-strain state of bending?
$$ in the tensile zone of concrete appeared cracks. At cracked sections, the stress in the tensile reinforcement area is perceived. (ss - Rs) Stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curvilinear;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and tensile zones is less than the limit, diagram the stresses in the tensile zone of curvilinear;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and tensile zones is less than the limit, a linear diagram;
$ stress in the tensile reinforcement in the cross section with a crack has reached the limit values (ss = Rs), stresses in the concrete compressed zone is equal to the tensile strength (sb = Rb), linear diagram.
$$$ 71 Indicate a stage of stress-strain state, which is used in the calculation of strength?
$$ third;
$ second;
$ first;
$ I-a.
$$$ 72 Specify methods of tension reinforcement to the concrete?
$$ mechanical;
$ electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermomechanical, mechanical;
$ automatic, electrothermomechanical, electrothermal.
$$$ 73 Specify methods of pretensioning of the reinforcements?
$$ mechanical, electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermal;
$ electrothermomechanical;
$ electric.
$$$ 74. Specify the stage of the stress-strain state, which is used to calculate the cracking?
$$ first;
$ second;
$ third;
$ I-a;
$$$ 75 Indicate stage of stress-strain state is used to calculate the crack width and deformation?
$$ second;
$ first;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 76 What is the purpose of the calculating ultimate limit state of the first group?
$$ to prevent any (brittle, ductile, fatigue) fracture, buckling shape and position;
$ to prevent the development of deformities and displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape or position;
$ to prevent brittle fracture.
$$$ 77 What is the purpose of calculating ultimate limit state of the second group?
$$ to prevent excessive opening of cracks, excessive movement;
$ to prevent structural failure from any external influence;
$ to prevent the development of excessive displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape and position.
$$$ 78 How loads are classified?
$$ dead and live;
$ dead and long-term;
$ long-term and short-term;
$ dead, live and special.
$$$ 79 Specify the reasons that cause the formation of inclined cracks?
$$ main tensile stresses;
$ stresses perpendicular to the rod axis (y);
$ stresses in the direction of axes x and y;
$ stresses along the axis of the rod (x).
$$$ 80 Specify the load included in special combinations?
$$ dead, long-term, short-term and one of the specials;
$ long-term and possible short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ short-term and special.
$$$ 81 Principle of reinforced concrete?
$$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and steel reinforcement, rationally located in the structures for the perception of tensile and, in some cases, and compression forces;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement, located arbitrarily in the cross section of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement that is located only in compressed zones of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement placed in the centre of gravity of the cross section of the element.
$$$ 82 Factors ensuring the joint operation of concrete and reinforcement?
$$ similar to those of the coefficients of linear expansion, of grip between concrete and reinforcement, protecting the reinforcement against corrosion and other external influences;
$ shrinkage and creep of concrete, the adhesion of concrete with reinforcement, protection of reinforcement against mechanical impact;
$ use of reinforcement periodic profile, the compression of the reinforcement due to shrinkage, the same coefficients of linear expansion;
$ protection of the reinforcement from external influences (corrosion, high temperature, mechanical), high strength concrete in compression, low strength of concrete in tension.
$$$ 83 How depends the strength of concrete from time to time?
$$ under favorable conditions the strength of concrete increases;
$ increases whatever the conditions;
$ the strength of concrete is reduced;
$ the strength of concrete does not change over time.
$$$ 84 Effect on concrete strength of stress?
$$ strength of concrete in compression is greater than in tension;
$ the strength of concrete in tension more than in compression;
$ the strength of concrete is the same in compression and in tension;
$ the strength of concrete are the same for dense concrete.
$$$ 85 What is called the class of concrete strength?
$$ temporary compressive strength of concrete cubes with size 150 mm rib, tested after 28 days of storage at a temperature of температуре 20 ± 20С With the statistical variability;
$ temporary resistance to axial compression of concrete prisms at the age of 28 days;
$ average value of tensile concrete compression test cubes standard;
$ temporary resistance to axial tension specimens at age of 28 days, taking into account statistical variability.
$$$ 86 What is shrinkage of concrete?
$$ the decrease in the volume of concrete hardening in air;
$ the decrease in hardening in water;
$ the decrease at high temperatures;
$ the increase of volume during solidification in the water.
$$$ 87 What is called creep of concrete?
$$ the increase in inelastic strain with time at constant stress;
$ the decrease in deformation of the loaded specimen over time;
$ the increase in the elastic deformation under the influence of long-acting load;
$ increase in deformation under load over time.
$$$ 88 Yield strength of steel?
$$ stress at which strain increases without load change;
$ stress up to which the material acts elastically;
$ stress at which permanent deformation amount to 0. 02%;
$ stress at which there is a gap element.
$$$ 89 What distinguishes prism strength from cube?
$$ less;
$ equal;
$ more;
$ are equal if the height of the prism is 2 times the height of the cube.
$$$ 90 What is the difference between strength of concrete tensile strength of concrete in compression?
$$ less;
$ more;
$ equal;
$ less only for lightweight concrete.
$$$ 91 What class is a plain reinforcement?
$$ A-I;
$ A-II;
$ A-III;
$ A-IV.
$$$ 92 What are the signs classified reinforcements?
$$ strength and deformability;
$ the chemical composition;
$ deformability;
$ strength.
$$$ 93 Specify the class of hot rolled reinforcement periodic profile?
$$ А-II…А-VI;
$ А-I;
$ Вр-I;
$ Вр-II.
$$$ 94 Specify the class of cold-drawn wire reinforcement with periodic profile?
$$ Вр-I, Вр-II;
$ А-III, А-IV;
$ A-I, A-II;
$ В-II.
$$$ 95 Specify the class of reinforcement cold-drawn plain profile?
$$ В-II;
$ Ат-IV, Ат-V;
$ Вр-I, Вр-II
$ A-I, А-III.
$$$ 96 For what purpose on the surface of the reinforcement creates a different kind of profile (ridges, bumps, etc. )?
$$ to improve the adhesion of the reinforcement with the concrete;
$ to improve the strength properties;
$ saving;
$ to improve weldability.
$$$ 97 Purpose of the thickness of the protective layer.
$$ enable collaboration reinforcement with concrete and to protect reinforcement from corrosion, high temperatures, mechanical damage;
$ to protect the reinforcement from corrosion;
$ to protect the reinforcement from mechanical damage;
$ protect the reinforcements from sudden changes of temperature.
$$$ 98 Goal of creating a prestressed reinforced concrete?
$$ to improve the crack resistance and stiffness, to ensure the use of high-strength reinforcement;
$ increase the carrying capacity of the element;
$ to increase the toughness and reduce the shrinkage strain;
$ to increase the strength of concrete.
$$$ 99 What characterizes the end of the first stage of stress-strain state of bending?
$$ stress in concrete stretched zone reached the ultimate strength (Rbt), in the compressed zone sb< Rb, linear diagram;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and stretched zones are changed according to the linear law (triangular diagram);
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone sb< Rb, in the tensile zone cracks;
$ the stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb=Rb) in the tensile zone is equal to the tensile strength (sbt=Rbt).
$$$ 100 The second stage is characterized by the stress-strain state of bending…
$$ in the tensile zone of concrete cracks. At cracked sections, the stress in the tensile reinforcement area is perceived. ((ss - Rs) Stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curvilinear;
$ stress in concrete is compressed and stretched zones is less than the limit, diagram the stresses in the tensile zone of curvilinear;
$ stress in concrete is compressed and stretched zones is less than the limit, a linear diagram;
$ stress in the tensile reinforcement in the cross section with a crack has reached the limit values (ss = Rs), stresses in the concrete compressed zone is equal to the tensile strength (sb=Rb), linear diagram.
$$$ 101 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state are used to calculate the strength?
$$ third;
$ second;
$ first;
$ I-a.
$$$ 102 What characterizes the third stage of the stress-strain state of bending?
$$ stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb = Rb), curvilinear stress diagram, the stress in the reinforcement is stretched zone has reached the physical or conditional yield strength;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is linear, the tension in the stretched zone reinforcement is less than yield stress;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit ((sb< Rb), the diagram is curved, the tension in the stretched zone reinforcement equals the yield stress.
$$$ 103 Main methods of creating pre-stress in the reinforcement?
$$ mechanical, electrothermomechanical, electrothermal;
$ electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermomechanical, mechanical;
$ mechanical, electrothermal.
$$$ 104 How to create pre-stressed concrete?
$$ tension reinforcement in abutments and concrete;
$ tension reinforcement to the concrete previously fabricated structures;
$ tension reinforcement at abutments with the subsequent concreting;
$ tension reinforcement with the help of winding machines.
$$$ 105 How changes the stress state of the reinforcement in the precast structures over time?
$$ reduces;
$ does not change;
$ increases;
$ change depends on initial stress values.
$$$ 106 What stress loss in the reinforcement occur before and during concrete prestressing under tension to the concrete?
$$ 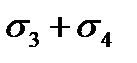 ;
;
$ 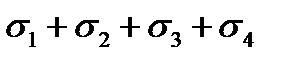 ;
;
$ 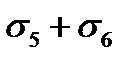 ;
;
$ 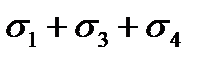 .
.
$$$ 107 What stress loss in the reinforcement occurs after prestressing of the concrete during pretensioning?
$$ 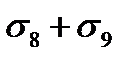 ;
;
$ 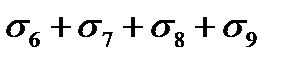 ;
;
$ 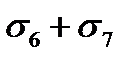 ;
;
$ 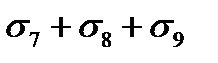 .
.
$$$ 108 What stress loss in the reinforcement occurs before and after prestressing of the concrete during pretensioning?
$$ 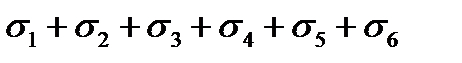 ;
;
$ 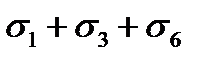 ;
;
$ 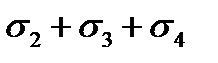 ;
;
$ 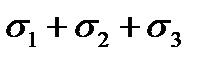 .
.
$$$ 109 What the stress loss in the reinforcement occur after the compression of the concrete in tension to the concrete?
$$ 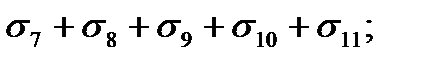
$ 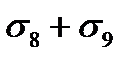 ;
;
$ 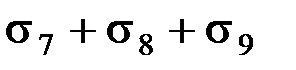 ;
;
$ 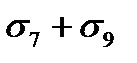 .
.
$$$ 110 Purpose of the calculation of the ultimate limit state of the first group?
$$ to prevent any (brittle, ductile, fatigue) fracture, buckling shape and position;
$ to prevent the development of deformities and displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape or position;
$ to prevent brittle fracture.
$$$ 111 Purpose of the calculation of the ultimate limit state of the second group?
$$ to prevent excessive opening of cracks, excessive movement;
$ to prevent structural failure from any external influence;
$ to prevent the development of excessive displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape and position.
$$$ 112 Classification of loads?
$$ dead and live;
$ dead and long-term;
$ long-term and short-term;
$ dead, live and special.
$$$ 113 Classification of live loads?
$$ long, short and special;
$ dead and long-term;
$ dead, live and special;
$ long-term and short-term.
$$$ 114 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state is used to calculate the cracking?
$$ first;
$ second;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 115 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state is used to calculate the crack width and deformation?
$$ second;
$ first;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 116 What is the purpose of introducing the partial safety factor for load?
$$ to account for variability of loads;
$ to account for the nature of the impact loads on the structure;
$ to account for the magnitude of loads;
$ to identify the loads class.
$$$ 117 What are the possible changes of the safety factor on the load gf?
$$ can be greater than 1, can be less than 0;
$ less than 1;
$ equals 1;
$ greater than 1.
$$$ 118 Design loads?
$$ establish multiplying the normative load by the safety factor q = qn g f;
$ set at their nominal values;
$ set norms with a given probability of exceedance;
$ establish dividing of the normative load by the safety factor 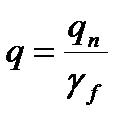 ;
;
$$$ 119 How are classified live loads?
$$ long-term, short-term and special;
$ short-term and special;
$ long-term and special;
$ short-term and long-term.
$$$ 120 What loads are in the main combinations?
$$ dead, long-term and short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ dead and long-term;
$ dead.
$$$ 121 Which loads are included in the special combinations?
$$ dead, long-term and possible short-term and one of the specials;
$ long-term and possible short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ short-term and special.
$$$ 122 According to what limit state group calculation the design resistance is equal to normative?
$$ the second group of limit states;
$ the first group of limit states;
$ in the calculation of strength;
$ when calculating the deformations.
$$$ 123 To which is introduced a boundary height of the compressed zone in bending?
$$ to clarify on what condition works the section (on the case I or case II of the third stage);
$ to ensure the strength of the element in the compressed zone;
$ to ensure the strength of the element in the tensile zone;
$ to ensure the strength of the element on both zones.
$$$ 124 Purpose of transverse reinforcement in bending elements?
$$ for the perception of the principal tensile stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of main compressive stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of tangential stresses;
$ for the perception of tensile stresses normal to the sections.
$$$ 125 Purpose of the longitudinal reinforcement in bending elements?
$$ for perception mainly tensile stresses and, in some cases, compressive in the normal section;
$ for the perception of compressive stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of the principal tensile stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of shear stresses.
$$$ 126 In some cases, resort to the installation of double reinforcements?
$$ low strength of concrete in compressed zone;
$ insufficient strength of concrete in tension zone;
$ low strength of tension reinforcement;
$ insufficient area of tension reinforcement.
$$$ 127 Which strength conditions at bending for rectangular section is correct 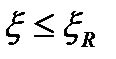 ?
?
$$ 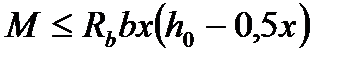 ;
;
$ 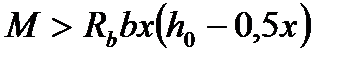 ;
;
$ 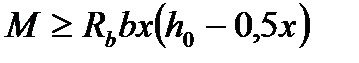 ;
;
$ 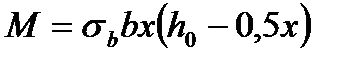 .
.
$$$ 128 What are the constructive requirements, ensuring the strength of the inclined sections on bending moment?
$$ longitudinal tension reinforcement should be brought to the supports, and ensures its reliable anchoring;
$ part of the longitudinal tensile reinforcement should be brought to the supports, and ensures its reliable anchoring;
$ longitudinal tension reinforcement should be brought to the supports;
$ part of the longitudinal reinforcement should be brought to the supports, additional transverse reinforcement is placed.
$$$ 129 Under what conditions is provided the strength of the inclined sections to the action of bending moment?
$$ 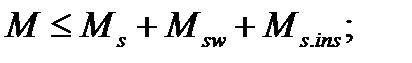
$ 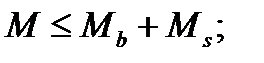
$ 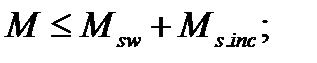
$ 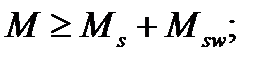
$$$ 130 Under what conditions is provided the strength of the inclined sections to the action of shear force?
$$ 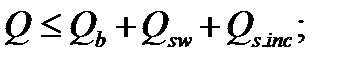
$ 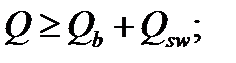
$ 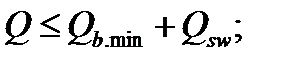
$ 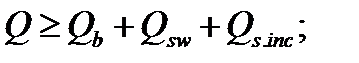
$$$ 131 Reasons that cause the formation of inclined cracks?
$$ main tensile stresses;
$ stresses perpendicular to the rod axis (y);
$ stresses in the direction of axes x and y;
$ stresses along the axis of the rod (x).
$$$ 132 Specify the correct dependency in determining the reinforcement ratio of bending elements.
$$ 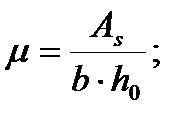
$ 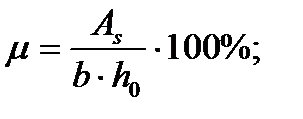
$ 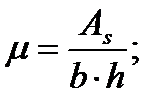
$ 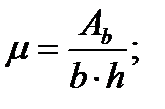
$$$ 133 What kind of structures are assigned grade of concrete on frost resistance?
$$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of alternate freezing and thawing;
$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ for all;
$ requirements of thermal insulation.
$$$ 134 What kind of structures are assigned grade of concrete on water resistance?
$$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of the transverse freezing and thawing;
$ requirements insulation;
$ for self-stressed frames
$$$ 135 What kind of structures in the project is specified the class of concrete on strength under axial compression?
$$ for all;
$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of alternate freezing and thawing;
$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ requirements of thermal insulation.
$$$ 136 In which cases are assigned the class of concrete strength on axial tension?
$$ when this feature will be essential and controlled at the production;
$ for all;
$ requirements insulation;
$ requirements limitations permeability.
$$$ 137 Design resistance of the transverse reinforcement (stirrups, bent bars) is reduced compared to Rs regardless of the type and class of reinforcement on the coefficient of working conditions, equals to:
$$ 0. 8
$ 0. 9
$ 0. 85
$ 0. 95
$$$ 138 When in the bent element arise inclined cracks near the supports?
$$ 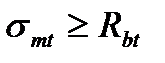
$ 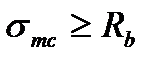
$ 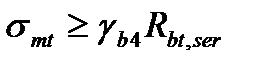
$ 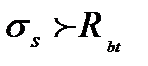
$$$ 139 For the strength of the concrete element along an inclined compressed strip between the inclined cracks must be performed the condition
$$ 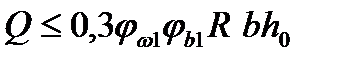
$ 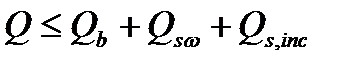
$ 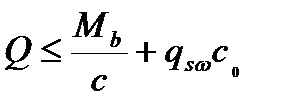
$ 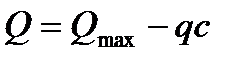
$$$ 140 Calculation of strength of reinforced concrete elements for inclined crack at the action of the transverse forces produced by the formula
$$ 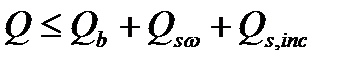
$ 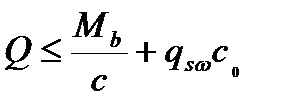
$ 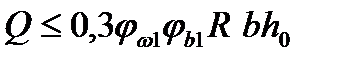
$ 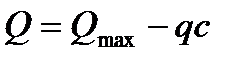
$$$ 141 Most rational shape of cross sections of bent prestressed elements is
$$ square
$ rectangular
$ I-shaped
$ trapezoid
$$$ 142 Definition of concrete?
$$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and steel reinforcement, rationally located in the structures for the perception of tensile and, in some cases, and compression forces;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement, located arbitrarily in the cross section of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement that is located only in compressed zones of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement placed in the centre of gravity of the cross section of the element.
$$$ 143 How the joint work of concrete and reinforcement is provided?
$$ similar to those of the coefficients of linear expansion, of the grip between reinforcement and concrete, protecting the reinforcement against corrosion and other external influences;
$ shrinkage and creep of concrete, the adhesion of concrete with reinforcement, protection of reinforcement against mechanical impacts;
$ use of reinforcement periodic profile, the compression of the reinforcement due to shrinkage, the same coefficients of linear expansion;
$ protection of the reinforcement from external influences (corrosion, high temperature, mechanical), high strength concrete in compression, low strength of concrete in tension.
$$$ 144 Class of concrete on strength?
$$ temporary compressive strength of concrete cubes with size 150 mm, tested after 28 days of storage at a temperature of 20 ± 2 °С including the statistical variability;
$ temporary resistance to axial compression of concrete prisms at the age of 28 days;
$ average value of tensile concrete compression test cubes standard;
$ temporary resistance to axial tension specimens at age of 28 days, taking into account statistical variability.
$$$ 145 Classification of reinforcements?
$$ strength and deformability;
$ chemical composition;
$ deformability;
$ strength.
$$$ 146 Specify the class of a plain reinforcement?
$$ A-I;
$ A-II;
$ A-III;
$ A-IV.
$$$ 147 Describe the end of the first stage of stress-strain state at bending?
$$ stress in concrete of tension zone reached the ultimate strength (Rbt), in the compressed zone sb< Rb, linear diagram;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and stretched zones are changed according to the linear law (triangular diagram);
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone sb< Rb, in the tensile zone cracks;
$ the stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb = Rb) in the tensile zone is equal to the tensile strength (sbt = Rbt).
$$$ 148 What for the different profiles on the surface of the reinforcement (ribs, bumps, etc. ) are created?
$$ to improve the adhesion of the reinforcement with the concrete;
$ to improve the strength properties;
$ to improve the deformation properties;
$ to improve weldability.
$$$ 149 Describe the third stage of the stress-strain state at bending?
$$ stress in the concrete of compressed zone equal to the ultimate (sb = Rb), curvilinear stress diagram, the stress in the reinforcement of tension zone has reached the physical or conditional yield strength;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is linear, the stress in the stretched zone reinforcement is less than yield stress;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curved, the stress in the reinforcement of tension zone equals the yield stress.
$$$ 150 Describe the second stage of the stress-strain state of bending?
$$ in the tensile zone of concrete appeared cracks. At cracked sections, the stress in the tensile reinforcement area is perceived. (ss - Rs) Stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curvilinear;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and tensile zones is less than the limit, diagram the stresses in the tensile zone of curvilinear;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and tensile zones is less than the limit, a linear diagram;
$ stress in the tensile reinforcement in the cross section with a crack has reached the limit values (ss = Rs), stresses in the concrete compressed zone is equal to the tensile strength (sb = Rb), linear diagram.
$$$ 151 Indicate a stage of stress-strain state, which is used in the calculation of strength?
$$ third;
$ second;
$ first;
$ I-a.
$$$ 152 Specify methods of tension reinforcement to the concrete?
$$ mechanical;
$ electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermomechanical, mechanical;
$ automatic, electrothermomechanical, electrothermal.
$$$ 153 Specify methods of pretensioning of the reinforcements?
$$ mechanical, electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermal;
$ electrothermomechanical;
$ electric.
$$$ 154. Specify the stage of the stress-strain state, which is used to calculate the cracking?
$$ first;
$ second;
$ third;
$ I-a;
$$$ 155 Indicate stage of stress-strain state is used to calculate the crack width and deformation?
$$ second;
$ first;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 156 What is the purpose of the calculating ultimate limit state of the first group?
$$ to prevent any (brittle, ductile, fatigue) fracture, buckling shape and position;
$ to prevent the development of deformities and displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape or position;
$ to prevent brittle fracture.
$$$ 157 What is the purpose of calculating ultimate limit state of the second group?
$$ to prevent excessive opening of cracks, excessive movement;
$ to prevent structural failure from any external influence;
$ to prevent the development of excessive displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape and position.
$$$ 158 How loads are classified?
$$ dead and live;
$ dead and long-term;
$ long-term and short-term;
$ dead, live and special.
$$$ 159 Specify the reasons that cause the formation of inclined cracks?
$$ main tensile stresses;
$ stresses perpendicular to the rod axis (y);
$ stresses in the direction of axes x and y;
$ stresses along the axis of the rod (x).
$$$ 160 Specify the load included in special combinations?
$$ dead, long-term, short-term and one of the specials;
$ long-term and possible short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ short-term and special.
$$$ 161 Principle of reinforced concrete?
$$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and steel reinforcement, rationally located in the structures for the perception of tensile and, in some cases, and compression forces;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement, located arbitrarily in the cross section of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement that is located only in compressed zones of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement placed in the centre of gravity of the cross section of the element.
$$$ 162 Factors ensuring the joint operation of concrete and reinforcement?
$$ similar to those of the coefficients of linear expansion, of grip between concrete and reinforcement, protecting the reinforcement against corrosion and other external influences;
$ shrinkage and creep of concrete, the adhesion of concrete with reinforcement, protection of reinforcement against mechanical impact;
$ use of reinforcement periodic profile, the compression of the reinforcement due to shrinkage, the same coefficients of linear expansion;
$ protection of the reinforcement from external influences (corrosion, high temperature, mechanical), high strength concrete in compression, low strength of concrete in tension.
$$$ 163 How depends the strength of concrete from time to time?
$$ under favorable conditions the strength of concrete increases;
$ increases whatever the conditions;
$ the strength of concrete is reduced;
$ the strength of concrete does not change over time.
$$$ 164 Effect on concrete strength of stress?
$$ strength of concrete in compression is greater than in tension;
$ the strength of concrete in tension more than in compression;
$ the strength of concrete is the same in compression and in tension;
$ the strength of concrete are the same for dense concrete.
$$$ 165 What is called the class of concrete strength?
$$ temporary compressive strength of concrete cubes with size 150 mm rib, tested after 28 days of storage at a temperature of температуре 20 ± 20С With the statistical variability;
$ temporary resistance to axial compression of concrete prisms at the age of 28 days;
$ average value of tensile concrete compression test cubes standard;
$ temporary resistance to axial tension specimens at age of 28 days, taking into account statistical variability.
$$$ 166 What is shrinkage of concrete?
$$ the decrease in the volume of concrete hardening in air;
$ the decrease in hardening in water;
$ the decrease at high temperatures;
$ the increase of volume during solidification in the water.
$$$ 167 What is called creep of concrete?
$$ the increase in inelastic strain with time at constant stress;
$ the decrease in deformation of the loaded specimen over time;
$ the increase in the elastic deformation under the influence of long-acting load;
$ increase in deformation under load over time.
$$$ 168 Yield strength of steel?
$$ stress at which strain increases without load change;
$ stress up to which the material acts elastically;
$ stress at which permanent deformation amount to 0. 02%;
$ stress at which there is a gap element.
$$$ 169 What distinguishes prism strength from cube?
$$ less;
$ equal;
$ more;
$ are equal if the height of the prism is 2 times the height of the cube.
$$$ 170 What is the difference between strength of concrete tensile strength of concrete in compression?
$$ less;
$ more;
$ equal;
$ less only for lightweight concrete.
$$$ 171 What class is a plain reinforcement?
$$ A-I;
$ A-II;
$ A-III;
$ A-IV.
$$$ 172 What are the signs classified reinforcements?
$$ strength and deformability;
$ the chemical composition;
$ deformability;
$ strength.
$$$ 173 Specify the class of hot rolled reinforcement periodic profile?
$$ А-II…А-VI;
$ А-I;
$ Вр-I;
$ Вр-II.
$$$ 174 Specify the class of cold-drawn wire reinforcement with periodic profile?
$$ Вр-I, Вр-II;
$ А-III, А-IV;
$ A-I, A-II;
$ В-II.
$$$ 175 Specify the class of reinforcement cold-drawn plain profile?
$$ В-II;
$ Ат-IV, Ат-V;
$ Вр-I, Вр-II
$ A-I, А-III.
$$$ 176 For what purpose on the surface of the reinforcement creates a different kind of profile (ridges, bumps, etc. )?
$$ to improve the adhesion of the reinforcement with the concrete;
$ to improve the strength properties;
$ saving;
$ to improve weldability.
$$$ 177 Purpose of the thickness of the protective layer.
$$ enable collaboration reinforcement with concrete and to protect reinforcement from corrosion, high temperatures, mechanical damage;
$ to protect the reinforcement from corrosion;
$ to protect the reinforcement from mechanical damage;
$ protect the reinforcements from sudden changes of temperature.
$$$ 178 Goal of creating a prestressed reinforced concrete?
$$ to improve the crack resistance and stiffness, to ensure the use of high-strength reinforcement;
$ increase the carrying capacity of the element;
$ to increase the toughness and reduce the shrinkage strain;
$ to increase the strength of concrete.
$$$ 179 What characterizes the end of the first stage of stress-strain state of bending?
$$ stress in concrete stretched zone reached the ultimate strength (Rbt), in the compressed zone sb< Rb, linear diagram;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and stretched zones are changed according to the linear law (triangular diagram);
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone sb< Rb, in the tensile zone cracks;
$ the stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb=Rb) in the tensile zone is equal to the tensile strength (sbt=Rbt).
$$$ 180 The second stage is characterized by the stress-strain state of bending…
$$ in the tensile zone of concrete cracks. At cracked sections, the stress in the tensile reinforcement area is perceived. ((ss - Rs) Stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curvilinear;
$ stress in concrete is compressed and stretched zones is less than the limit, diagram the stresses in the tensile zone of curvilinear;
$ stress in concrete is compressed and stretched zones is less than the limit, a linear diagram;
$ stress in the tensile reinforcement in the cross section with a crack has reached the limit values (ss = Rs), stresses in the concrete compressed zone is equal to the tensile strength (sb=Rb), linear diagram.
$$$ 181 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state are used to calculate the strength?
$$ third;
$ second;
$ first;
$ I-a.
$$$ 182 What characterizes the third stage of the stress-strain state of bending?
$$ stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb = Rb), curvilinear stress diagram, the stress in the reinforcement is stretched zone has reached the physical or conditional yield strength;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is linear, the tension in the stretched zone reinforcement is less than yield stress;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit;
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone is less than the limit ((sb< Rb), the diagram is curved, the tension in the stretched zone reinforcement equals the yield stress.
$$$ 183 Main methods of creating pre-stress in the reinforcement?
$$ mechanical, electrothermomechanical, electrothermal;
$ electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermomechanical, mechanical;
$ mechanical, electrothermal.
$$$ 184 How to create pre-stressed concrete?
$$ tension reinforcement in abutments and concrete;
$ tension reinforcement to the concrete previously fabricated structures;
$ tension reinforcement at abutments with the subsequent concreting;
$ tension reinforcement with the help of winding machines.
$$$ 185 How changes the stress state of the reinforcement in the precast structures over time?
$$ reduces;
$ does not change;
$ increases;
$ change depends on initial stress values.
$$$ 186 What stress loss in the reinforcement occur before and during concrete prestressing under tension to the concrete?
$$ 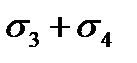 ;
;
$ 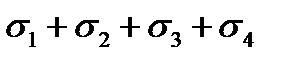 ;
;
$ 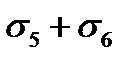 ;
;
$ 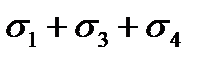 .
.
$$$ 187 What stress loss in the reinforcement occurs after prestressing of the concrete during pretensioning?
$$ 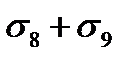 ;
;
$ 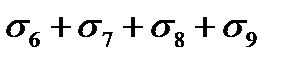 ;
;
$ 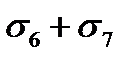 ;
;
$ 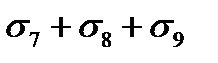 .
.
$$$ 188 What stress loss in the reinforcement occurs before and after prestressing of the concrete during pretensioning?
$$ 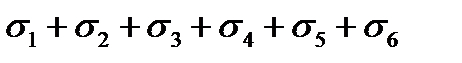 ;
;
$ 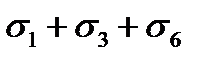 ;
;
$ 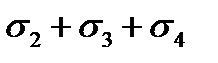 ;
;
$ 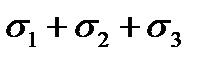 .
.
$$$ 189 What the stress loss in the reinforcement occur after the compression of the concrete in tension to the concrete?
$$ 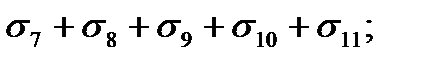
$ 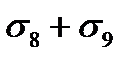 ;
;
$ 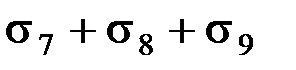 ;
;
$ 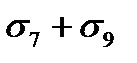 .
.
$$$ 190 Purpose of the calculation of the ultimate limit state of the first group?
$$ to prevent any (brittle, ductile, fatigue) fracture, buckling shape and position;
$ to prevent the development of deformities and displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape or position;
$ to prevent brittle fracture.
$$$ 191 Purpose of the calculation of the ultimate limit state of the second group?
$$ to prevent excessive opening of cracks, excessive movement;
$ to prevent structural failure from any external influence;
$ to prevent the development of excessive displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape and position.
$$$ 192 Classification of loads?
$$ dead and live;
$ dead and long-term;
$ long-term and short-term;
$ dead, live and special.
$$$ 193 Classification of live loads?
$$ long, short and special;
$ dead and long-term;
$ dead, live and special;
$ long-term and short-term.
$$$ 194 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state is used to calculate the cracking?
$$ first;
$ second;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 195 Which of the three stages of stress-strain state is used to calculate the crack width and deformation?
$$ second;
$ first;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 196 What is the purpose of introducing the partial safety factor for load?
$$ to account for variability of loads;
$ to account for the nature of the impact loads on the structure;
$ to account for the magnitude of loads;
$ to identify the loads class.
$$$ 197 What are the possible changes of the safety factor on the load gf?
$$ can be greater than 1, can be less than 0;
$ less than 1;
$ equals 1;
$ greater than 1.
$$$ 198 Design loads?
$$ establish multiplying the normative load by the safety factor q = qn g f;
$ set at their nominal values;
$ set norms with a given probability of exceedance;
$ establish dividing of the normative load by the safety factor 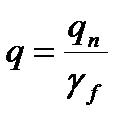 ;
;
$$$ 199 How are classified live loads?
$$ long-term, short-term and special;
$ short-term and special;
$ long-term and special;
$ short-term and long-term.
$$$ 200 What loads are in the main combinations?
$$ dead, long-term and short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ dead and long-term;
$ dead.
$$$ 201 Which loads are included in the special combinations?
$$ dead, long-term and possible short-term and one of the specials;
$ long-term and possible short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ short-term and special.
$$$ 202 According to what limit state group calculation the design resistance is equal to normative?
$$ the second group of limit states;
$ the first group of limit states;
$ in the calculation of strength;
$ when calculating the deformations.
$$$ 203 To which is introduced a boundary height of the compressed zone in bending?
$$ to clarify on what condition works the section (on the case I or case II of the third stage);
$ to ensure the strength of the element in the compressed zone;
$ to ensure the strength of the element in the tensile zone;
$ to ensure the strength of the element on both zones.
$$$ 204 Purpose of transverse reinforcement in bending elements?
$$ for the perception of the principal tensile stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of main compressive stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of tangential stresses;
$ for the perception of tensile stresses normal to the sections.
$$$ 205 Purpose of the longitudinal reinforcement in bending elements?
$$ for perception mainly tensile stresses and, in some cases, compressive in the normal section;
$ for the perception of compressive stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of the principal tensile stresses in the inclined section;
$ for the perception of shear stresses.
$$$ 206 In some cases, resort to the installation of double reinforcements?
$$ low strength of concrete in compressed zone;
$ insufficient strength of concrete in tension zone;
$ low strength of tension reinforcement;
$ insufficient area of tension reinforcement.
$$$ 207 Which strength conditions at bending for rectangular section is correct 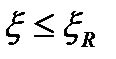 ?
?
$$ 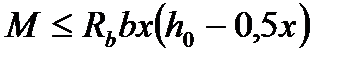 ;
;
$ 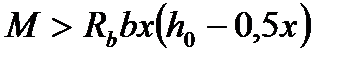 ;
;
$ 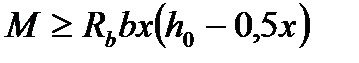 ;
;
$ 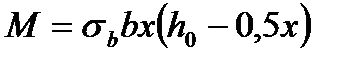 .
.
$$$ 208 What are the constructive requirements, ensuring the strength of the inclined sections on bending moment?
$$ longitudinal tension reinforcement should be brought to the supports, and ensures its reliable anchoring;
$ part of the longitudinal tensile reinforcement should be brought to the supports, and ensures its reliable anchoring;
$ longitudinal tension reinforcement should be brought to the supports;
$ part of the longitudinal reinforcement should be brought to the supports, additional transverse reinforcement is placed.
$$$ 209 Under what conditions is provided the strength of the inclined sections to the action of bending moment?
$$ 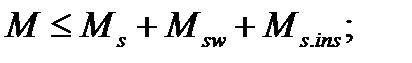
$ 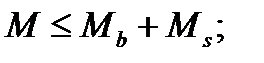
$ 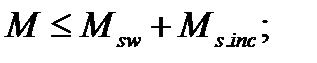
$ 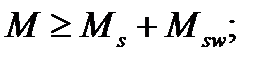
$$$ 210 Under what conditions is provided the strength of the inclined sections to the action of shear force?
$$ 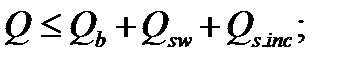
$ 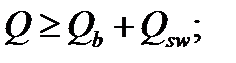
$ 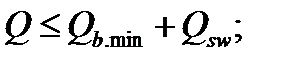
$ 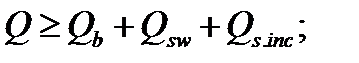
$$$ 211 Reasons that cause the formation of inclined cracks?
$$ main tensile stresses;
$ stresses perpendicular to the rod axis (y);
$ stresses in the direction of axes x and y;
$ stresses along the axis of the rod (x).
$$$ 212 Specify the correct dependency in determining the reinforcement ratio of bending elements.
$$ 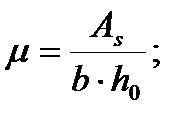
$ 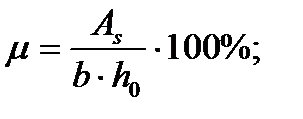
$ 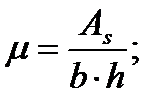
$ 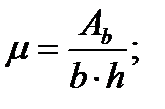
$$$ 213 What kind of structures are assigned grade of concrete on frost resistance?
$$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of alternate freezing and thawing;
$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ for all;
$ requirements of thermal insulation.
$$$ 214 What kind of structures are assigned grade of concrete on water resistance?
$$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of the transverse freezing and thawing;
$ requirements insulation;
$ for self-stressed frames
$$$ 215 What kind of structures in the project is specified the class of concrete on strength under axial compression?
$$ for all;
$ exposed in a moist condition to the action of alternate freezing and thawing;
$ requirements that limit permeability;
$ requirements of thermal insulation.
$$$ 216 In which cases are assigned the class of concrete strength on axial tension?
$$ when this feature will be essential and controlled at the production;
$ for all;
$ requirements insulation;
$ requirements limitations permeability.
$$$ 217 Design resistance of the transverse reinforcement (stirrups, bent bars) is reduced compared to Rs regardless of the type and class of reinforcement on the coefficient of working conditions, equals to:
$$ 0. 8
$ 0. 9
$ 0. 85
$ 0. 95
$$$ 218 When in the bent element arise inclined cracks near the supports?
$$ 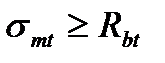
$ 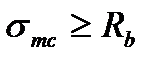
$ 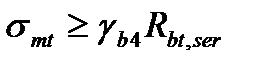
$ 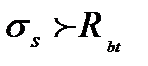
$$$ 219 For the strength of the concrete element along an inclined compressed strip between the inclined cracks must be performed the condition
$$ 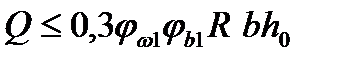
$ 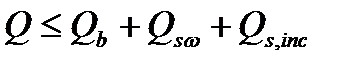
$ 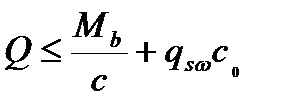
$ 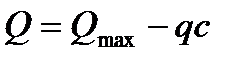
$$$ 220 Calculation of strength of reinforced concrete elements for inclined crack at the action of the transverse forces produced by the formula
$$ 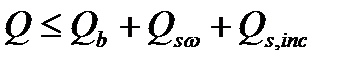
$ 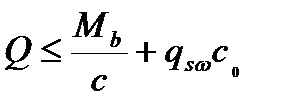
$ 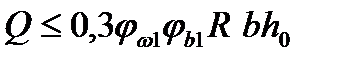
$ 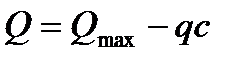
$$$ 221 Most rational shape of cross sections of bent prestressed elements is
$$ square
$ rectangular
$ I-shaped
$ trapezoid
$$$ 222 Definition of concrete?
$$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and steel reinforcement, rationally located in the structures for the perception of tensile and, in some cases, and compression forces;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement, located arbitrarily in the cross section of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement that is located only in compressed zones of the element;
$ reinforced concrete consists of concrete and reinforcement placed in the centre of gravity of the cross section of the element.
$$$ 223 How the joint work of concrete and reinforcement is provided?
$$ similar to those of the coefficients of linear expansion, of the grip between reinforcement and concrete, protecting the reinforcement against corrosion and other external influences;
$ shrinkage and creep of concrete, the adhesion of concrete with reinforcement, protection of reinforcement against mechanical impacts;
$ use of reinforcement periodic profile, the compression of the reinforcement due to shrinkage, the same coefficients of linear expansion;
$ protection of the reinforcement from external influences (corrosion, high temperature, mechanical), high strength concrete in compression, low strength of concrete in tension.
$$$ 224 Class of concrete on strength?
$$ temporary compressive strength of concrete cubes with size 150 mm, tested after 28 days of storage at a temperature of 20 ± 2 °С including the statistical variability;
$ temporary resistance to axial compression of concrete prisms at the age of 28 days;
$ average value of tensile concrete compression test cubes standard;
$ temporary resistance to axial tension specimens at age of 28 days, taking into account statistical variability.
$$$ 225 Classification of reinforcements?
$$ strength and deformability;
$ chemical composition;
$ deformability;
$ strength.
$$$ 226 Specify the class of a plain reinforcement?
$$ A-I;
$ A-II;
$ A-III;
$ A-IV.
$$$ 227 Describe the end of the first stage of stress-strain state at bending?
$$ stress in concrete of tension zone reached the ultimate strength (Rbt), in the compressed zone sb< Rb, linear diagram;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and stretched zones are changed according to the linear law (triangular diagram);
$ stresses in the concrete compressed zone sb< Rb, in the tensile zone cracks;
$ the stress in the concrete compressed zone equal to the marginal (sb = Rb) in the tensile zone is equal to the tensile strength (sbt = Rbt).
$$$ 228 What for the different profiles on the surface of the reinforcement (ribs, bumps, etc. ) are created?
$$ to improve the adhesion of the reinforcement with the concrete;
$ to improve the strength properties;
$ to improve the deformation properties;
$ to improve weldability.
$$$ 229 Describe the third stage of the stress-strain state at bending?
$$ stress in the concrete of compressed zone equal to the ultimate (sb = Rb), curvilinear stress diagram, the stress in the reinforcement of tension zone has reached the physical or conditional yield strength;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is linear, the stress in the stretched zone reinforcement is less than yield stress;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit;
$ stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curved, the stress in the reinforcement of tension zone equals the yield stress.
$$$ 230 Describe the second stage of the stress-strain state of bending?
$$ in the tensile zone of concrete appeared cracks. At cracked sections, the stress in the tensile reinforcement area is perceived. (ss - Rs) Stresses in the concrete of compressed zone is less than the limit (sb< Rb), the diagram is curvilinear;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and tensile zones is less than the limit, diagram the stresses in the tensile zone of curvilinear;
$ stress in the concrete is compressed and tensile zones is less than the limit, a linear diagram;
$ stress in the tensile reinforcement in the cross section with a crack has reached the limit values (ss = Rs), stresses in the concrete compressed zone is equal to the tensile strength (sb = Rb), linear diagram.
$$$ 231 Indicate a stage of stress-strain state, which is used in the calculation of strength?
$$ third;
$ second;
$ first;
$ I-a.
$$$ 232 Specify methods of tension reinforcement to the concrete?
$$ mechanical;
$ electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermomechanical, mechanical;
$ automatic, electrothermomechanical, electrothermal.
$$$ 233 Specify methods of pretensioning of the reinforcements?
$$ mechanical, electrothermal, electrothermomechanical;
$ electrothermal;
$ electrothermomechanical;
$ electric.
$$$ 234. Specify the stage of the stress-strain state, which is used to calculate the cracking?
$$ first;
$ second;
$ third;
$ I-a;
$$$ 235 Indicate stage of stress-strain state is used to calculate the crack width and deformation?
$$ second;
$ first;
$ third;
$ I-a.
$$$ 236 What is the purpose of the calculating ultimate limit state of the first group?
$$ to prevent any (brittle, ductile, fatigue) fracture, buckling shape and position;
$ to prevent the development of deformities and displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape or position;
$ to prevent brittle fracture.
$$$ 237 What is the purpose of calculating ultimate limit state of the second group?
$$ to prevent excessive opening of cracks, excessive movement;
$ to prevent structural failure from any external influence;
$ to prevent the development of excessive displacements;
$ to prevent the loss of stability of shape and position.
$$$ 238 How loads are classified?
$$ dead and live;
$ dead and long-term;
$ long-term and short-term;
$ dead, live and special.
$$$ 239 Specify the reasons that cause the formation of inclined cracks?
$$ main tensile stresses;
$ stresses perpendicular to the rod axis (y);
$ stresses in the direction of axes x and y;
$ stresses along the axis of the rod (x).
$$$ 240 Specify the load included in special combinations?
$$ dead, long-term, short-term and one of the specials;
$ long-term and possible short-term;
$ dead and short-term;
$ short-term and special.
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|