
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Taxes. International trade
Taxes
An excise tax is a tax on sales of a good or service.
The incidence of a tax is a measure of who really pays it.
The higher the price elasticity of supply and the lower the price elasticity of demand, the heavier the burden of an excise tax on consumers. The lower the price elasticity of supply and the higher the price elasticity of demand, the heavier the burden on producers.
A tax rate is the amount of tax people are required to pay per unit of whatever is being taxed.

The administrative costs of a tax are the resources used by government to collect the tax, and by taxpayers to pay it, over and above the amount of the tax, as well as to evade it.

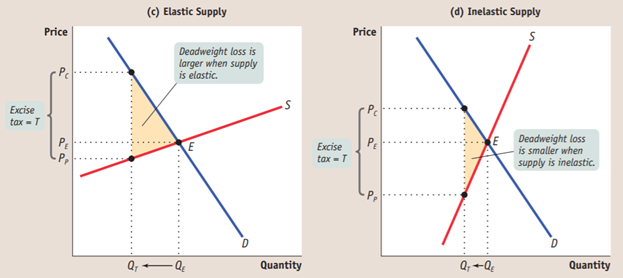
An excise tax generates tax revenue equal to the tax rate times the number of units of the good or service transacted but reduces consumer and producer surplus.
The government tax revenue collected is less than the loss in total surplus because the tax creates inefficiency by discouraging some mutually beneficial transactions.
The difference between the tax revenue from an excise tax and the reduction in total surplus is the deadweight loss from the tax. The total amount of inefficiency resulting from a tax is equal to the dead- weight loss plus the administrative costs of the tax.
The larger the number of transactions prevented by a tax, the larger the deadweight loss. As a result, taxes on goods with a greater price elasticity of supply or demand, or both, generate higher deadweight losses. There is no deadweight loss when the number of transactions is unchanged by the tax.
According to the benefits principle of tax fairness, those who benefit from public spending should bear the burden of the tax that pays for that spending.
According to the ability-to-pay principle of tax fairness, those with greater ability to pay a tax should pay more tax.
A lump-sum tax is the same for every- one, regardless of any actions people take.
In a well-designed tax system, there is a trade-off between equity and efficiency: the system can be made more efficient only by making it less fair, and vice versa.
The tax base is the measure or value, such as income or property value, that determines how much tax an individual or firm pays.
The tax structure specifies how the tax depends on the tax base.
Some important taxes and their tax bases are as follows:
· Income tax: a tax that depends on the income of an individual or family from wages and investments
· Payroll tax: a tax that depends on the earnings an employer pays to an employee
· Sales tax: a tax that depends on the value of goods sold (also known as an excise tax)
· Profits tax: a tax that depends on a firm’s profits
· Property tax: a tax that depends on the value of property, such as the value of a home
· Wealth tax: a tax that depends on an individual’s wealth
A proportional tax is the same percent- age of the tax base regardless of the taxpayer’s income or wealth.
A progressive tax takes a larger share of the income of high-income taxpayers than of low-income taxpayers.
A regressive tax takes a smaller share of the income of high-income taxpayers than of low-income taxpayers.
The marginal tax rate is the percentage of an increase in income that is taxed away.
International trade
Goods and services purchased from other countries are imports; goods and services sold to other countries are exports.
Globalization is the phenomenon of growing economic linkages among countries.
The Ricardian model of international trade analyzes international trade under the assumption that opportunity costs are constant.
Autarky is a situation in which a country does not trade with other countries.
The factor intensity of production of a good is a measure of which factor is used in relatively greater quantities than other factors in production.
According to the Heckscher–Ohlin model, a country has a comparative advantage in a good whose production is intensive in the factors that are abundantly available in that country.
Sources of Comparative Advantage:
· Differences in climate
· Differences in factor endowments
· Differences in technology
The domestic demand curve shows how the quantity of a good demanded by domestic consumers depends on the price of that good.
The domestic supply curve shows how the quantity of a good supplied by domestic producers depends on the price of that good.
The world price of a good is the price at which that good can be bought or sold abroad.
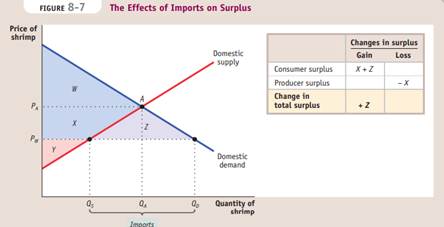
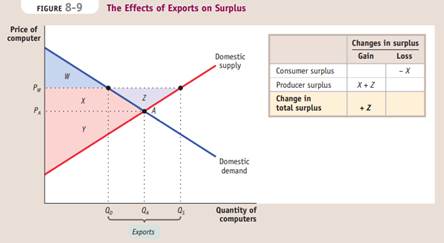
Exporting industries produce goods and services that are sold abroad.
Import-competing industries produce goods and services that are also imported.
An economy has free trade when the government does not attempt either to reduce or to increase the levels of exports and imports that occur naturally as a result of supply and demand.
If the world price is lower than the autarky price, trade leads to imports and the domestic price falls to the world price. There are overall gains from trade because the gain in consumer surplus exceeds the loss in producer surplus.
If the world price is higher than the autarky price, trade leads to exports and the domestic price rises to the world price. There are overall gains from trade because the gain in producer surplus exceeds the loss in consumer surplus.
Policies that limit imports are known as trade protection or simply as protection.
A tariff is a tax levied on imports.
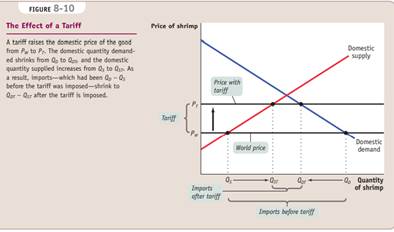
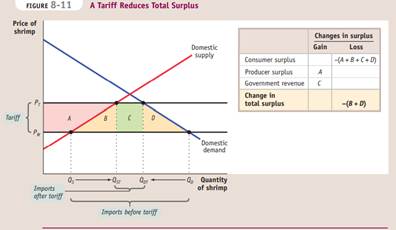
An import quota is a legal limit on the quantity of a good that can be imported.
International trade agreements are treaties in which a country promises to engage in less trade protection against the exports of other countries in return for a promise by other countries to do the same for its own exports.
The North American Free Trade Agreement, or NAFTA, is a trade agreement among the United States, Canada, and Mexico.
The European Union, or EU, is a customs union among 27 European nations.
The World Trade Organization, or WTO, oversees international trade agreements and rules on disputes between countries over those agreements.
Offshore outsourcing takes place when businesses hire people in another country to perform various tasks.
|
|
|
© helpiks.su При использовании или копировании материалов прямая ссылка на сайт обязательна.
|