
- Автоматизация
- Антропология
- Археология
- Архитектура
- Биология
- Ботаника
- Бухгалтерия
- Военная наука
- Генетика
- География
- Геология
- Демография
- Деревообработка
- Журналистика
- Зоология
- Изобретательство
- Информатика
- Искусство
- История
- Кинематография
- Компьютеризация
- Косметика
- Кулинария
- Культура
- Лексикология
- Лингвистика
- Литература
- Логика
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Материаловедение
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Металлургия
- Метрология
- Механика
- Музыка
- Науковедение
- Образование
- Охрана Труда
- Педагогика
- Полиграфия
- Политология
- Право
- Предпринимательство
- Приборостроение
- Программирование
- Производство
- Промышленность
- Психология
- Радиосвязь
- Религия
- Риторика
- Социология
- Спорт
- Стандартизация
- Статистика
- Строительство
- Технологии
- Торговля
- Транспорт
- Фармакология
- Физика
- Физиология
- Философия
- Финансы
- Химия
- Хозяйство
- Черчение
- Экология
- Экономика
- Электроника
- Электротехника
- Энергетика
Matching!
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF BLOOD VESSELS. ARTERIAL HYPERTANSION.
1. Most cases of combined systolic and diastolic hypertension have no known cause and are therefore diagnosed as _____ hypertension.
a. primary
b. secondary
c. congenital
d. acquired
2. Arteriosclerosis raises the systolic pressure by:
a. increasing arterial distensibility and lumen diameter
b. increasing arterial distensibility and decreasing lumen diameter
c. decreasing arterial distensibility and increasing lumen diameter
d. decreasing arterial distensibility and lumen diameter
3. Factors associated with primary hypertension include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. family history of hypertension
b. black race
c. high dietary sodium intake
d. cigarette smoking
e. preeclampsia
4. All of the following represent risk factors for primary hypertension EXCEPT:
a. family history of hypertension
b. high potassium intake
c. black race
d. increased alcohol consumption
e. male gender
5. Elevations of systolic pressure alone are usually caused by:
a. increases in cardiac output
b. increases in total peripheral vascular resistance
c. a and b
d. none of the above
6. "Sudden death in a teen. Since there's no sign of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and since there's a suggestive history, I'm going to look for "bypass fibers" from atrium to ventricle, bypassing the bundle of His." This very smart pathologist was considering a diagnosis of
a. Amyloidosis
b. Wenckebach phenomenon
c. general adaptation syndrome
d. Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome
e. Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome
7. A 53-year-old woman is found on a routine physical examination to have vital signs with T 36.9° C, P 77/minute, R 15/minute, and BP 165/110 mmHg. There are no other significant findings. She has an abdominal ultrasound examination that shows the right kidney to be atrophic. Angiography reveals markedly reduced blood flow to the right renal artery from an occlusion at the orifice in the abdominal aorta. Which of the following laboratory findings is she most likely to have?
a. serum sodium of 161 mmol/L
b. serologic evidence of anti-cardiolipin antibody
c. prothrombin time of 25 seconds
d. plasma renin activity of 4.8 ng/mL/hr supine
a. serum lactic acid of 5.5 mmol/L
Matching!
Which kinds of arrhythmia are represented in Fig. 23.3? Match the numbered electrocardiogram patterns with their lettered denominations and descriptions.
| 1. | 
| 4. | 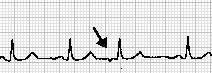
| |
| 2. | 
| 5. | 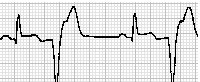
| |
| 3. | 
| 6. | 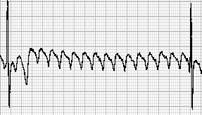
| |